A Review of HVAC System Optimization and Its Effects on Saving Total Energy Utilization of a Building
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.93.1.6482Keywords:
HVAC optimization, Control Parameters, Common Energy Model, Prescient Energy Model, Thermal Comfort, Optimization Models, PMV Index, EnergyPlusTMAbstract
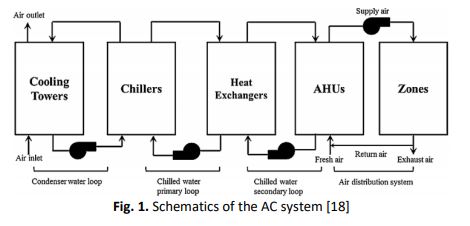
The paper illustrates the review on the optimizations studies of HVAC systems based on three main methods – HVAC operational variables optimization, optimization of control parameters in HVAC system and parameter optimization in building models. For the HVAC system’s operational variables, the optimization process is based on the common and prescient energy utilization models. Thus, by comparing both, the non-common HVAC system models can get better output of energy reduction. Based on most of the studies, the occupancies thermal comfort requirements, are represented by the indoor air quality (IAQ) or the predicted mean vote (PMV) indexes. Comparing both requirements, the PMV index had a better overall energy reduction output of 47% and estimated annual energy reduction of 2,769 kg/year. Meanwhile, in optimization of HVAC’s control parameters, its overall aim is to achieve a better response output of the HVAC system in order to prevent energy wastage. Among this different optimization’s controller, the fuzzy logic tuning optimization has a better overall energy reduction. On the other hand, the parameter optimization in building model approach is performed before the construction of the structure itself, where multiple construction parameters are considerations in the design. In overall, when different tools for building parameter and model optimization are compared, the EXRETopt by using PMV comfort index approximately reduces 62% of the energy utilization.
Downloads