Analysis of Energy and Mass Transport Flow of Ethyleneglycol (C2H6O2) Based Nanofluid over an Infinite Porous Plate
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.108.1.136157Keywords:
MHD, nanofluid, radiation absorption, Dufour effect, porous medium, chemical reactionAbstract
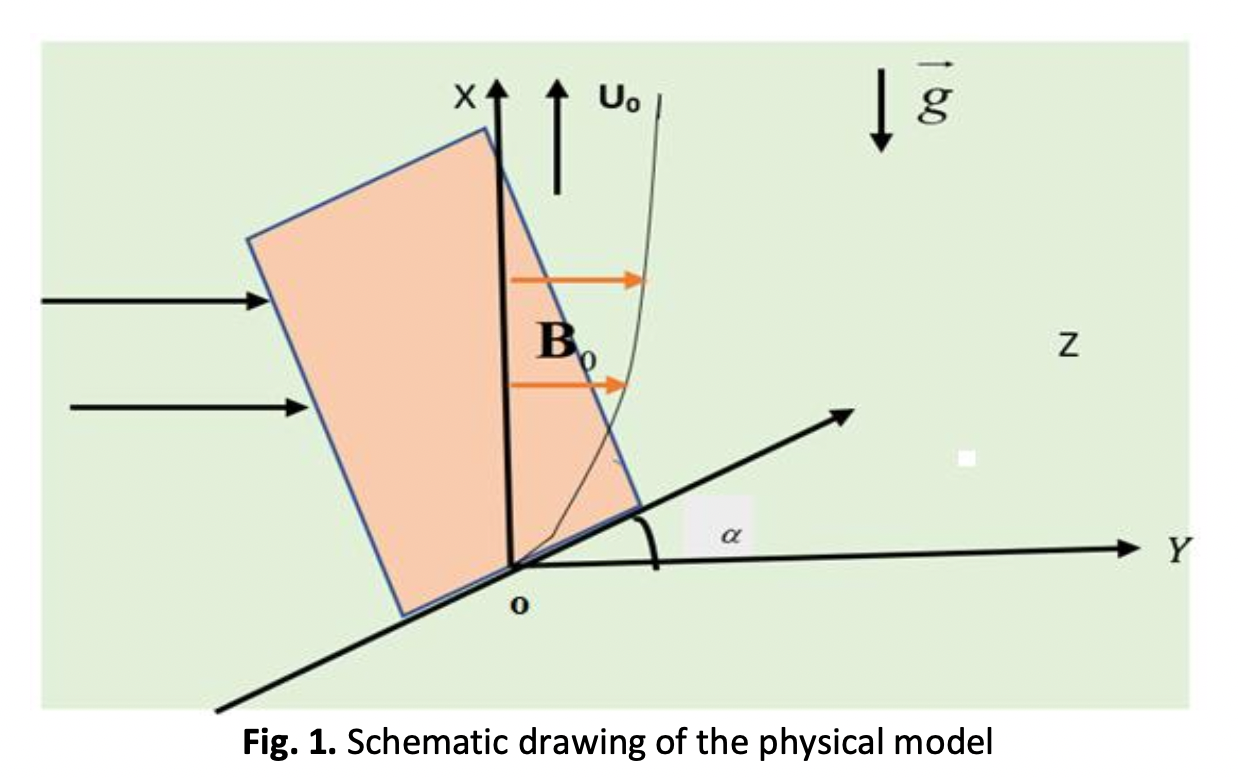
The main aim of this article is to analyze the flow properties of energy and mass transport flow of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) based nanofluid over an infinite porous plate. A constant velocity U0 is applied to the plate, and warmth and attention are unspecified to fluctuate harmonically as of a steady denote at the shield through occasion. Three kinds of fluid nanoparticles namely Cu-C2H6O2, CuO-C2H6O2 as well as TiO2-C2H6O2 nano fluids are used. Through graphs and tables, the impacts of different fluid flow parameters are examined. The new parameters added in this analysis are thermal radiation and the angle of inclination. The objective of this work is to derive exact solution by perturbation method and analyze the variations in the flow. The diffusion thermo parameter as well as the radiation absorption parameter have been observed to improve the speed, the hotness, plus the resistance between skin cells. An examination of the skin friction coefficient numerically in detail for the engineering industry. This development has main consequences for Particles of nanoscale. The solid particles have an elevated conductivity, which accounts for this of Cu, CuO than those of TiO2. In addition, by means of an augment in the substance response constraint, it is seen so as to the solutal border layer thickness decreases.
Downloads