The Significant Effect of Hydromagnetic on Carbon Nanotubes Based Nanofluids Flow and Heat Transfer Past a Porous Stretching/Shrinking Sheet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.106.1.5164Keywords:
CNTs nanofluids, heat transfer, shrinking/stretching sheet, hydromagnetic, porosityAbstract
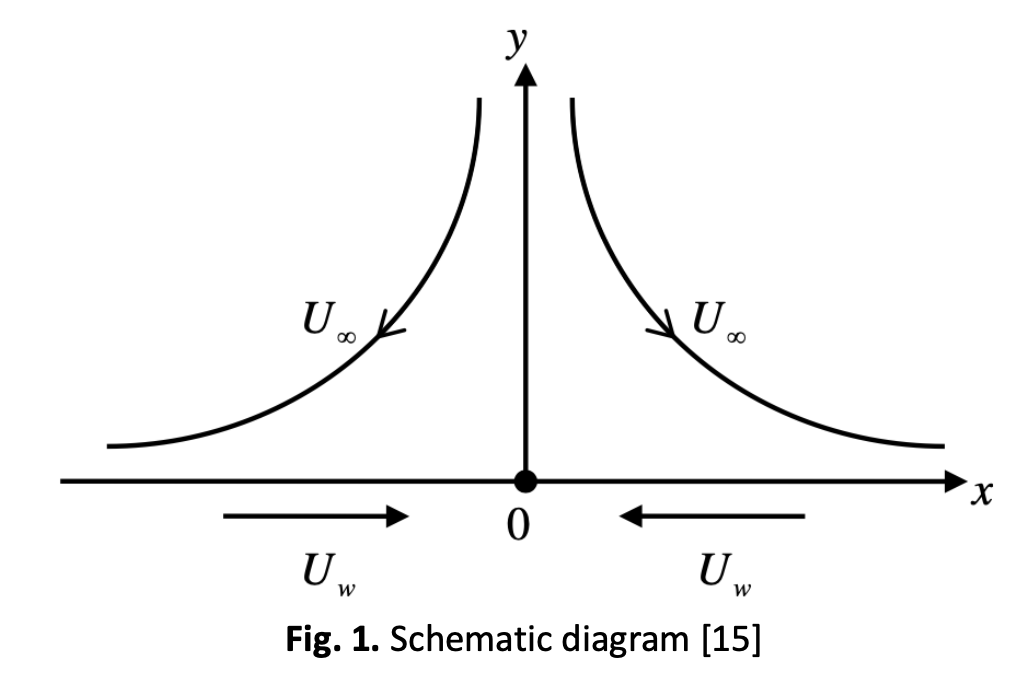
The 2D steady flow model of carbon nanotubes-based nanofluids and heat transfer past a porous stretchable or shrinkable sheet is studied analytically and numerically. A mathematical model that is governed by a system of partial differential equations (PDEs) subjected to boundary conditions is transformed into a system of dimensionless ordinary equations (ODEs). The non-dimensional ODEs system is solved using MATLAB bvp4c solver. The effect of various parameters such as magnetic field, porosity, the stretching/ shrinking velocity parameter, and CNTs volume friction on velocity and temperature profile, skin friction, Nusselt number and heat transfer rate are investigated numerically and the results are presented using graphical illustration. From the results, non-unique solutions are obtained in the cases where the sheet is shrunk, the magnetic parameter less than 0.1, or the porosity parameter is less than 30. Besides, the increment of magnetic field into the flow will increase both the skin friction and the heat transfer coefficient, while on the contrary, the decreasing in both the skin friction and the heat transfer coefficient will occur if the porosity parameter is raised. We are also showing that SWCNTs is more effective both in the skin friction and the heat transfer coefficient compared to MWCNTs.
Downloads