Static Analysis of Low Temperature Waste Heat Driven Three-bed Adsorption Chillers Potential for Building Cooling Application
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.112.2.174190Keywords:
Environmentally friendly cooling system, adsorption, condensation heat, silica-gel, building cooling systemAbstract
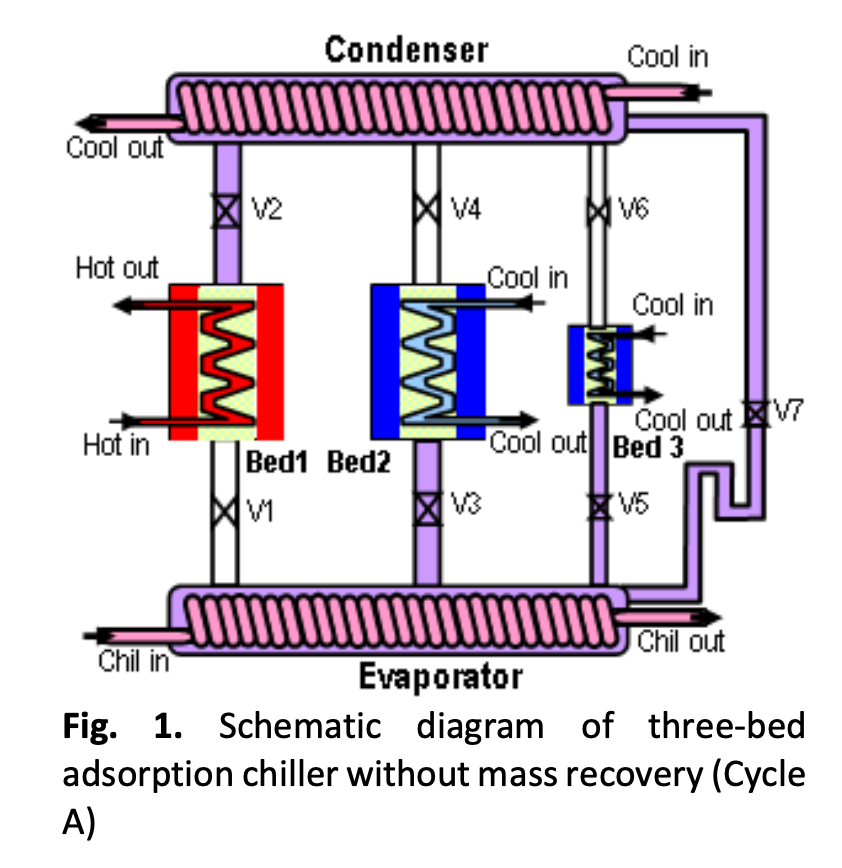
The adsorption cooling system is an environmentally friendly system because of non-CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) and non-HCFCs (hydrochlorofluorocarbons). The simulation developed is an adsorption system that can operate with a low temperature waste heat source so that this adsorption system can be applied to building cooling systems. The purpose of this research is to obtain the most effective and efficient cycle of three bed silica gel-water adsorption system with a low temperature heat source so that it has the potential for building applications. The method developed is by simulating various design combinations of three bed adsorption systems and simulating 6 (six) cycle types. Furthermore, those designs of silica gel-water based two different types of three-bed adsorption chiller has been analyzed statically. The performance of the chillers was investigated in terms of coefficient of performance (COP) and specific cooling effect (SCE) for heat source temperature between 60oC and 90oC. The result first shows that the performance data of the proposed chillers (Cycle E and Cycle F) were compared with those of other four different types of three-bed adsorption chiller with the same operating conditions. It was observed that the proposed chillers provided a higher SCE compared with other four assorted chillers. Second result show that The Cycle B obtained the higher COP comparing with the other cycles designed in this study. Thus, this system has a good potential to be developed for building cooling systems by utilizing heat waste.
Downloads