The Phenomenon of Flow and Heat Transfer in Annular Heat Exchanger on Plain Tube Condition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.100.2.146156Keywords:
Annular heat exchanger, Nusselt number, phenomena, flow, heat transferAbstract
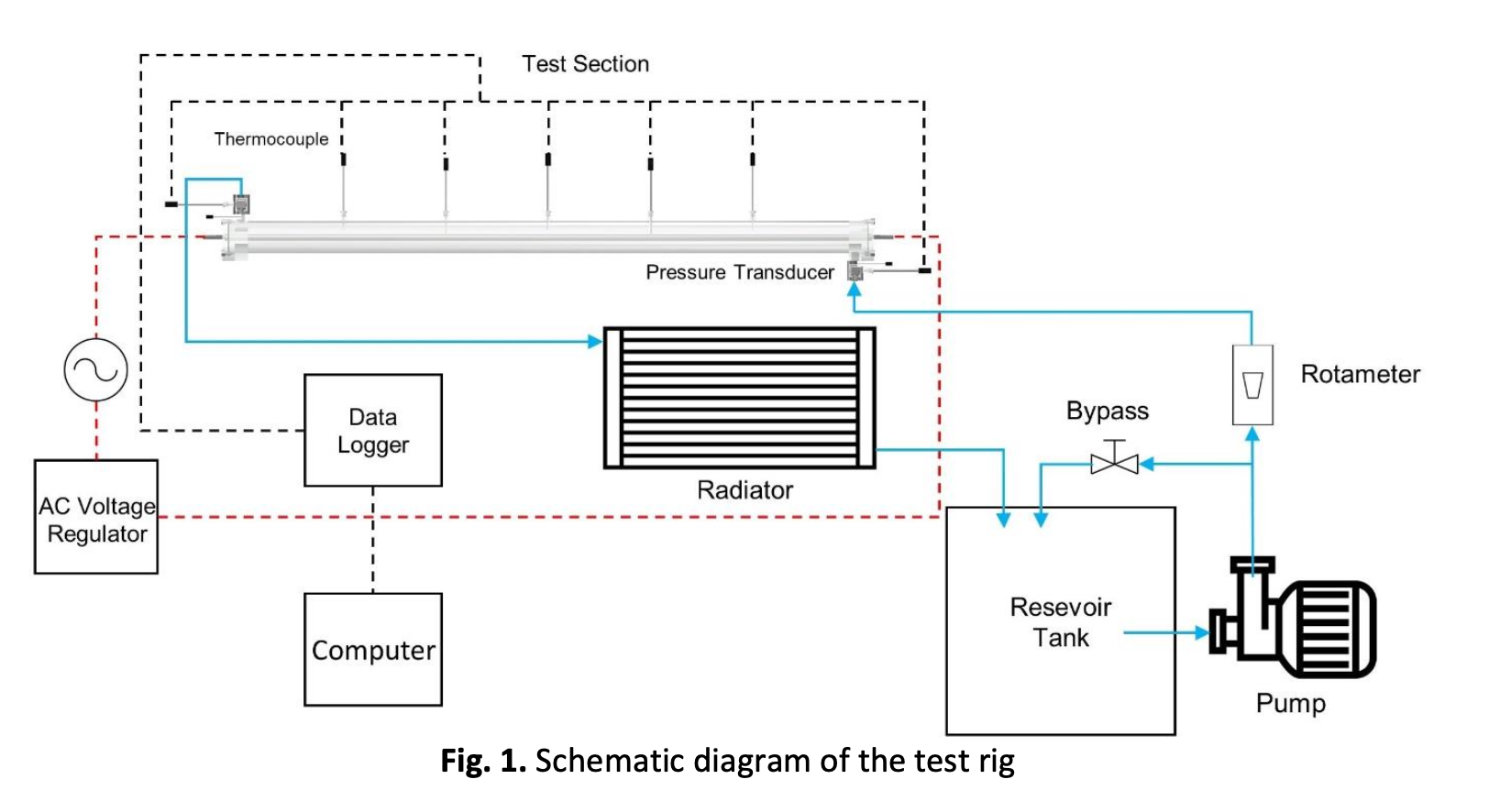
Advanced industrial development in technology necessitates using equipment that can effectively and efficiently transfer heat energy. A heat exchanger is the most common device used in industry to transfer heat energy. The Annular Heat Exchanger is one of the heat exchangers used in industry that is simple to manufacture and inexpensive to finance. The annular heat exchanger is commonly found in the food, beverage, chemical process, pharmaceutical, and refrigeration technology industries. This type of heat exchanger is used due to its simple design, easy to manufacture, and low cost. The presence of a heater in a concentric pipe with a straight construction is the general form. Experimentation was carried out in this study. A heater is used to transfer the heat, and there is a cold fluid flow through the annulus. The heater is linked to an AC Voltage Regulator and has five heat settings ranging from 400 W to 600 W. Simultaneously, cold fluid flows in the annulus via a closed system with six flow variations ranging from 2.5 GPM to 5 GPM. A cooling system is used to keep cold fluids at a constant temperature. The purpose of this research is to demonstrate the flow and heat transfer phenomena in an annular heat exchanger. This study obtained the average heat transfer convection coefficient, h, and Nusselt number, Nu. The steady-state conditions for the heat variations of 400 W, 500 W, and 600 W are 2400 s, 3600 s, and 5400 s, respectively. The flow calibration results in this apparatus experiment have an error of 0.05%. At a heat variation of 500 W and Reynolds number 10669, the highest average heat transfer convection coefficient (h) reaches 6703 W/m2K, and the average Nusselt number (Nu) of 314 is obtained. The Reynolds number of critical transition points for heat variations of 400 W, 450 W, 500 W, 550 W, and 600 W are 6986, 7125, 8444, 8616, and 10009, respectively.
Downloads