Optimization of the Antioxidant Properties of the Polyherbal Formulations
Keywords:
Antioxidant properties, PPH, FRAP, Optimization, TPCAbstract
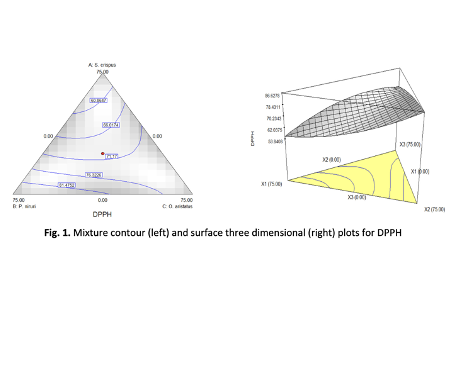
The secondary metabolites from plants have important biological and pharmacological activities such as anti-oxidative, anti-carcinogenic, and antibiotic. Plant extracts which are rich in polyphenol can be beneficial both towards product development and human health. They are well known of having high content of antioxidant compounds and have been recognized as having potential in reducing disease risk as antioxidant. The objective of this study is to optimize polyherbal extracts with antioxidant properties. It was conducted by involving leaves of Strobilanthes crispus (pecah beling), Phyllanthus niruri (dukung anak), Orthosiphon aristatus (misai kucing) and Stevia rebudiana through in-vitro assay. Polyherbal formulation was developed with 22 different formulations of various aqueous extracts proportion designated by using commercial statistical software package which is Design Expert 6.0.4. Antioxidant activities of the plants depend on the concentration of the antioxidant and also the structure and interaction between the antioxidant. Antioxidant properties of polyherbal formulation were identified spectrophotometrically through 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), Ferric Reduction Antioxidant Potential Assay (FRAP), and total phenolic content (TPC) assay. Most of the assay showed that O. aristatus has higher antioxidant properties than S. crispus, P. niruri and S. rebudiana but most of the polyherbal combination exhibit synergistic effect. Through optimization process, examination of the fit summary output indicates that quadratic model was statistically significant for the FRAP and TPC meanwhile DPPH was statistically significant for cubic model. From a series of formulation, the optimum mixture for antioxidant properties was revealed to be the extract mixture of 23.96% of S. crispus, 0.62% of P. niruri and 75.42% of O. aristatus with desirability of 0.985. Hence, through all the results obtained, the present study justifies these polyherbal formulations have promising antioxidant properties. This identification would be able to let the traditional medicine to be fully utilized and become much beneficial to human being.
Downloads