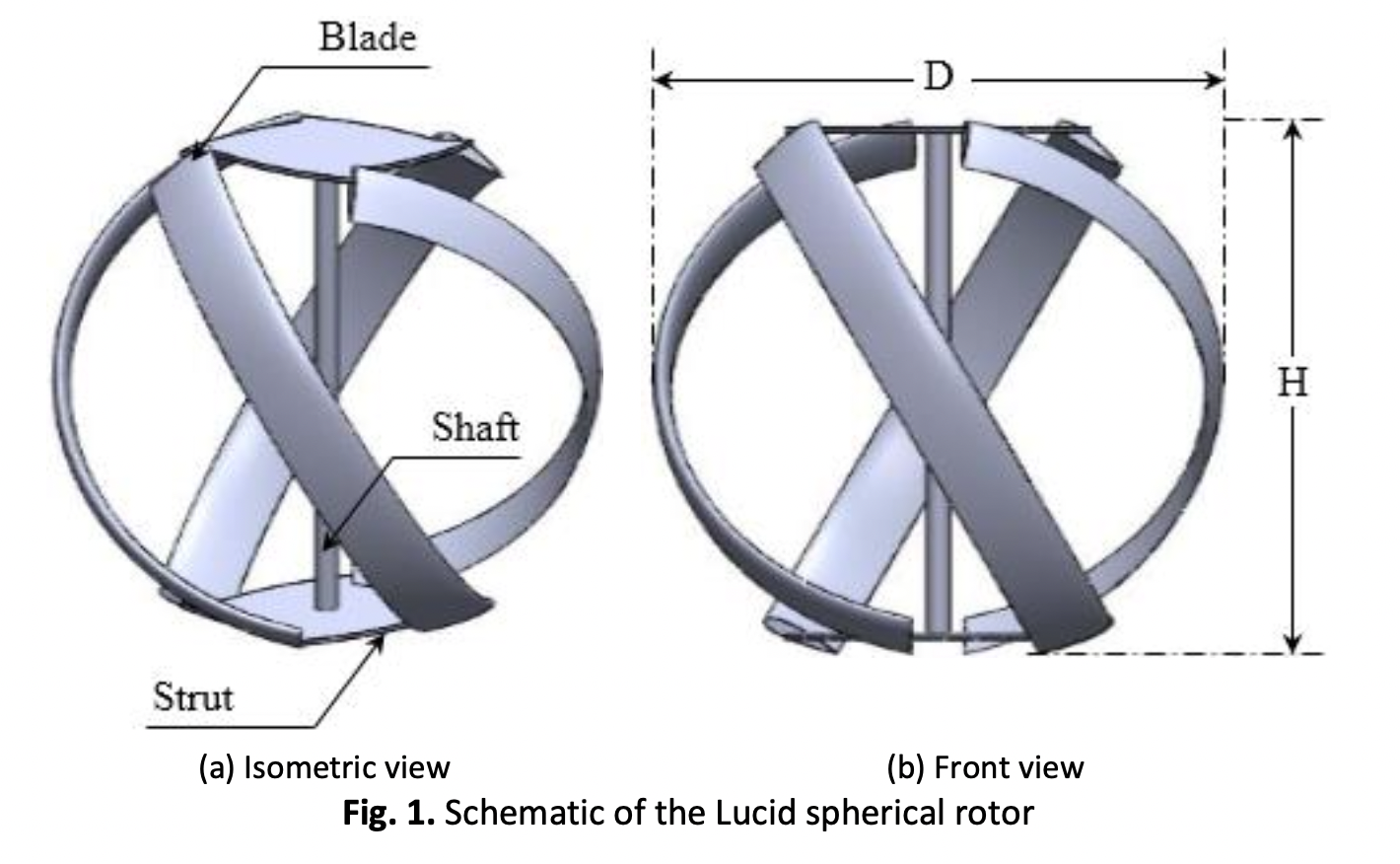
Effect of the Turbulence Model on the Computational Results of a Lucid Spherical Rotor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.113.1.2443Keywords:
Numerical simulations, URANS, turbulence models, Lucid spherical rotorAbstract
Due to the excessive increase in the energy demand, renewable energy has become an alternative for electricity production for industrial and domestic needs. Water energy has received significant investment as a sustainable and clean energy source. Lucid spherical rotors, a kind of hydro-power converter, are cross flow rotors designed to be mounted within a pipeline in order to gather excess energy available in gravity-fed water pipelines. This paper focuses on the effect of the numerical model parameters choice, namely the turbulence model, on the Lucid spherical rotor hydrodynamic characteristics. Numerical simulations were carried out through Ansys Fluent software 17.0 using the unsteady Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (URANS) equations. Four turbulence models: RNG k-ε, Realizable k-ε, SST k-ω and transition SST were tested. Performance characteristics in terms of torque and power coefficients in addition to hydrodynamic features of the flow around the considered rotor were analyzed. The adopted numerical model was validated based on previous experimental findings from the literature. It was found that the realizable k-ε model showed a good agreement with experimental results. Thus, it was adopted for the Lucid spherical rotor simulation. The obtained findings could provide further direction for researchers to use the Lucid spherical water turbine.
Downloads