Influence of Blade-Flow Interactions on Flow Behaviours and Blade Loading of an Automotive Mixed-Flow Turbine
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.105.1.131153Keywords:
Mixed-flow turbine, Fluid-Structure Interactions, Computational Fluid Dynamics, blade loading, secondary flowAbstract
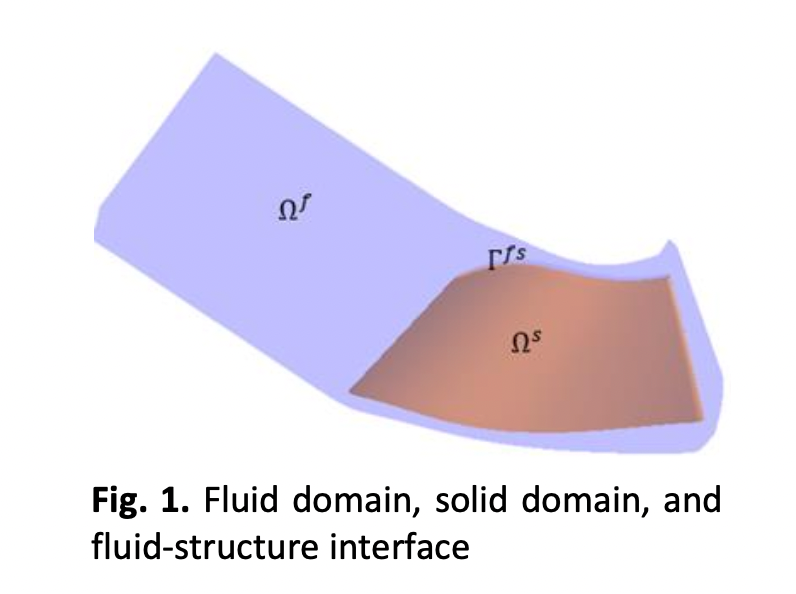
Mixed-flow turbine (MFT) is one type of turbines in automotive turbocharger. Multiple studies on turbine blades and flow interactions were done in this area but mainly focusing on structural responses and none on the fluid behaviours. The objectives of this paper are to compare and analyse the influence of blade-flow interactions on flow behaviours and blade loading at four MFT turbine operating conditions under steady state flow. Flow behaviours are indicated by appearances of secondary flows and blade loading is ratio of static pressure acting on turbine rotor blades over the total isentropic pressure at volute inlet. Blade loading represents capability of turbine blades to generate torque. Three validated simulations models using commercial software were developed, a non-coupled model and coupled models which consists of one-way and two-way coupled model. Non-coupled model assumes blades are rigid bodies and for coupled models, blades are deformable and share interfaces for interactions. Results show that there are differences in flow behaviours in non-coupled and coupled models that affect blade loading. Coupled models produce torque with range 1.33% to 0.60% lower than non-coupled model at most operating conditions. At 50% turbine design speed, average efficiency differences for non-coupled and coupled models to experiment data are 1.38% and 1.28% respectively. There is no significant difference in flow behaviours in one-way and two-way coupled models due to the stiffness of material of turbine blades is high but show minor differences in blade loading and torque.
Downloads