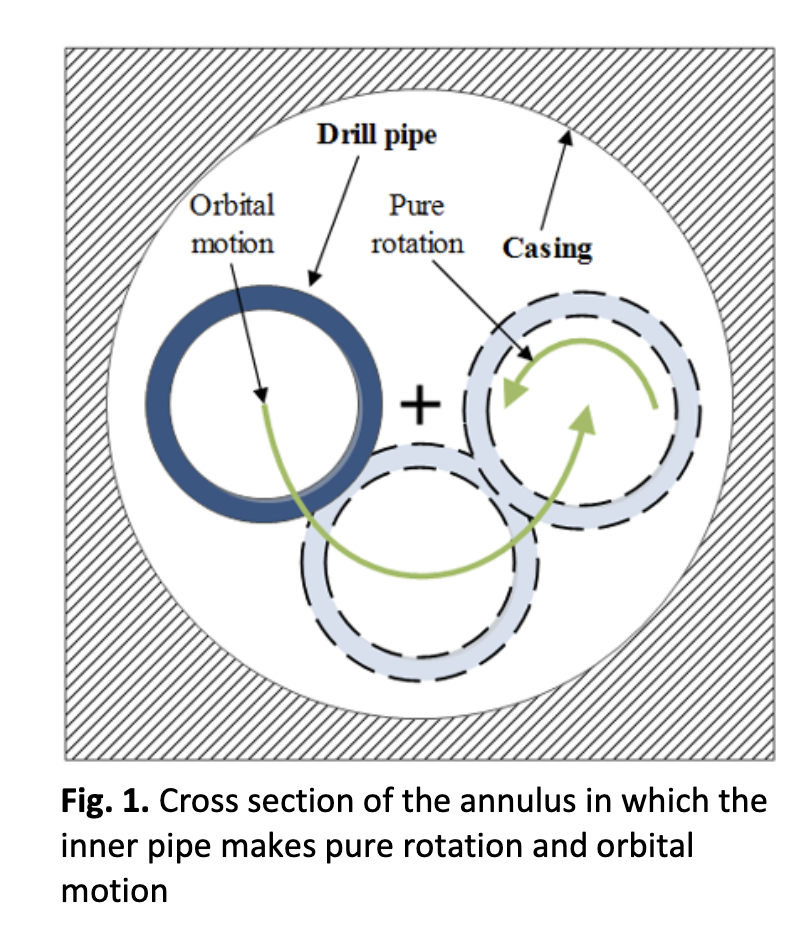
The Impact of Orbital Motion of Drill Pipe on Pressure Drop of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Eccentric Annulus
Keywords:
CFD approach, orbital motion, frictional pressure drop, non-Newtonian fluid, flow regimeAbstract
For all drilling operation method used to explore a well, the hydraulics program design associated to the well must be carried out carefully. A wrong estimation of pressure drop of the drilling fluid in the annular space can induce several problems, like: stuck pipe, lost circulation and insufficient hole cleaning. ANSYS Fluent 18.2 code based on the finite volume method (FVM) is employed to evaluate the orbital motion impact of drill pipe on frictional pressure drop of non-Newtonian fluids (Ostwald-de Waele and Herschel-Bulkley models) flowing in laminar and turbulent regimes where the inner cylinder (drill pipe) makes an orbital motion around the centre of the outer cylinder (casing) and pure rotation around its own axis. Moreover, impact of the eccentricity on frictional pressure drop is discussed. Numerical results exhibit that as the Reynolds number increases, effect of the orbital motion speed of the inner cylinder becomes more severe on frictional pressure drop of the Ostwald-de Waele fluid for laminar regime. However, after a certain speed, frictional pressure drop begins to decrease. In addition, increase of the eccentricity induces a decrease of frictional pressure drop of the Ostwald-de Waele fluid in which this effect is more pronounced when the inner cylinder makes orbital motion for both laminar and turbulent regimes.
Downloads