Air Flow Analysis and Effect of Angle on Rotation Vane Blade Through 90-Degree by Computational Fluid Dynamic
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.95.2.8498Keywords:
90° pipe bend, vane blade, numerical study, pressure dropAbstract
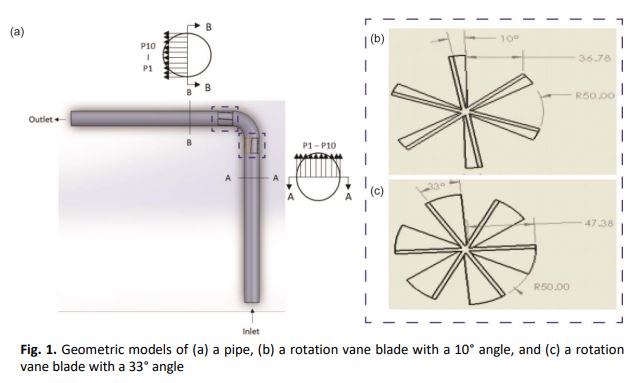
The effects of different angles of rotation vane blades on the flow characteristics in a pipe bend were numerically examined in this work using computational fluid analysis (CFD). The model's geometry included a straight inlet pipe of 1 m length, a 90° pipe bend with a 0.1 m cross-section diameter, a straight outlet pipe of 1 m length, and the installation of rotating vane blades at 10° and 33° angles. The simulation's input parameters include fluid viscosity (0.000017894 kg/m.s), fluid density (1.225 kg/m3), and inlet fluid velocity (10, 14, 20, 24, 26, and 30 m/s). The simulations' output parameters include velocity and pressure measured at two points: section A-A (before the pipe bend) and section B-B (after pipe bend). The findings demonstrate that the velocity and pressure distribution is somewhat uneven at section B-B owing to the presence of the rotating vane. The most efficient rotation vane blade angle is 10° since it has the lowest velocity, static pressure, and pressure drop.
Downloads