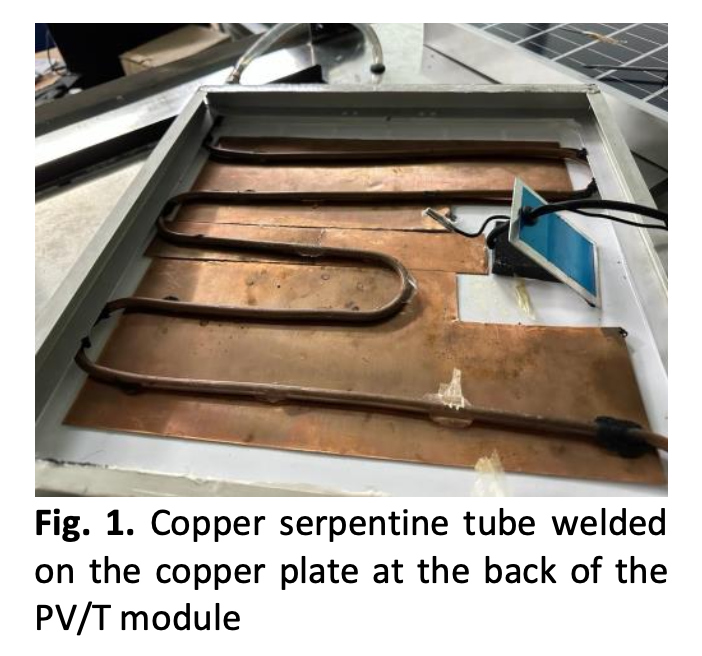
Performance Evaluation of Photovoltaic Thermal using MgO Nanofluid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.109.2.184209Keywords:
Electrical Efficiency, MgO Nanofluid, Overall Efficiency, Surfactant, Thermal EfficiencyAbstract
This study investigated the performance and efficiency of a photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) system utilizing a metal-based nanofluid, specifically MgO nanofluid. This research proposes MgO as nanoparticle to mix with base fluid because it demonstrated to have superior features with the highest thermal conductivity and lowest viscosity among the metal oxide. The nanofluid offered improved thermophysical properties that enhanced the PV/T system performance. The study focused on formulating a stable nanofluid, determining its thermophysical properties, and analysing the overall system performance. 0.2wt% MgO nanofluid were successfully developed and demonstrated excellent stability over a 14-day period by using a two-step method which 20 minutes of homogenization at 1000rpm and 30 minutes of ultrasonication. Tests were conducted to determine the thermal conductivity and viscosity of the nanofluid at various concentrations and temperatures. Results showed that increasing the concentration and temperature enhanced thermal conductivity, while viscosity increased with concentration but decreased with temperature. The thermal and electrical efficiencies of the PV/T system at various irradiances (200W/m2, 500W/m2 and 800W/m2), and flow rates (10L/h, 20L/h, 30L/h) were examined, calculated and compared between water and the MgO nanofluid as working fluids. At 10L/h, it was observed that nanofluid had the highest 74% of thermal efficiency increment compared to the water at 500W/m2 followed by 71% at 200w/m2 and 55% at 800W/m2. Also, Nanofluid demonstrated a 5% increase in electrical efficiency at 200W/m2, 2.1% increase at 500W/m2, and 1.9% increase at 800W/m2 compared to water. The nanofluid exhibited superior thermal and electrical efficiency compared to water, indicating its potential for improving system performance hence, surpassing the performance of a standalone PV system.
Downloads