Measurement of Spectral Match and Spatial Non-uniformity for Indoor Solar Simulator
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.100.1.98115Keywords:
Halogen lamp, spectral match, spatial non-uniformity, indoor solar simulatorAbstract
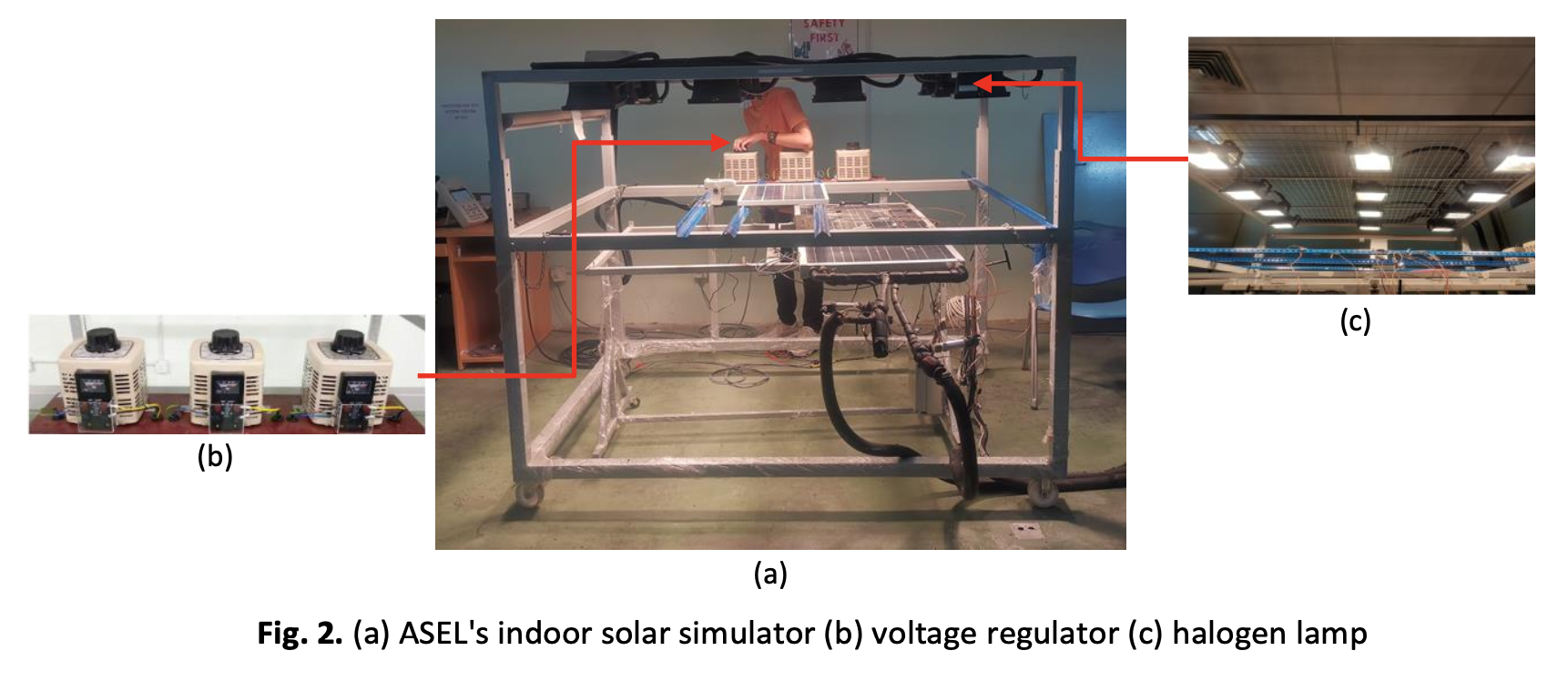
This paper presents a study on the measurement of spectral match and spatial non-uniformity of the indoor solar simulator available in Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM). This indoor solar simulator which was successfully fabricated at the Applied Solar Energy Laboratory (ASEL) had used the quartz tungsten halogen lamp as its only light source. Upon its fabrication, the reliability of ASEL’s solar simulator has not been proved yet as there is no concrete evidence that it had followed the international standard set for solar simulator. Therefore, the motivation of this study had been set to determine the characteristics of the indoor solar simulator in term of its spectral match and spatial non-uniformity. The literature review conducted has revealed that there are few methods that been practiced to determine both cases. For the spectral match test, the experimental works chosen for this research was the mathematical modelling method. Meanwhile, for the spatial non-uniformity test, irradiance mapping method was used where the reading of irradiance intensity at each coordinate across the map was measured. At the end of this study, it shows that at 400-500nm and 500-600 wavelength range, the value of spectral match value obtained was 0.40 and 1.46 respectively; whereas for 600-700nm range, the spectral match measured was beyond the standard range set. On the other hand, this study also reveals that the solar simulator was capable to produce 8.42% of spatial non-uniformity across the tested area of 104cm x 80cm. The average irradiance intensity recorded for this test was 981.98 W/m2.
Downloads