Convective Boundary Layer Flow of Williamson Hybrid Ferrofluid over a Moving Flat Plate with Viscous Dissipation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.112.1.176188Keywords:
Williamson hybrid ferrofluid, blood based, moving plate, viscous dissipationAbstract
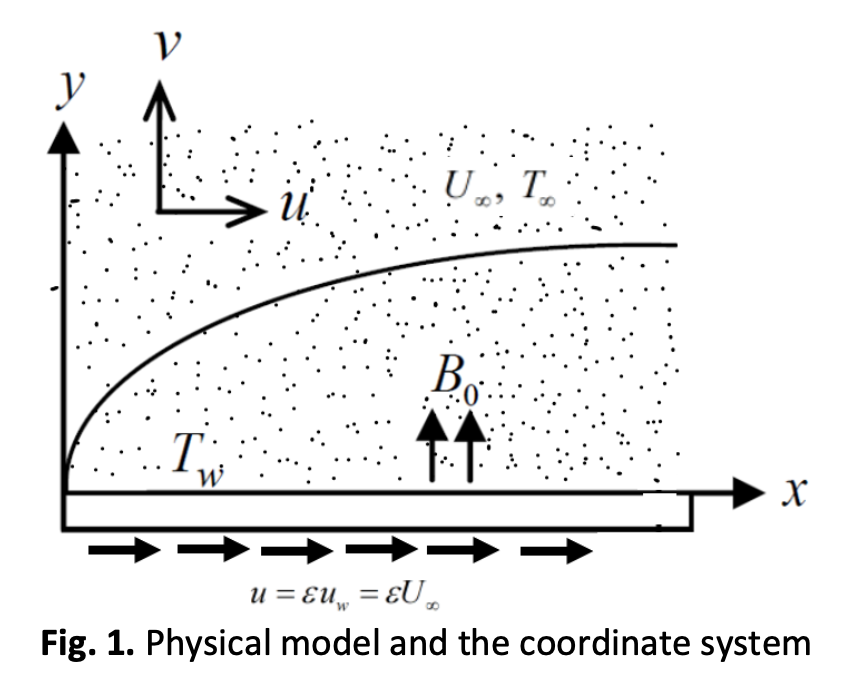
Specifically, the oxide ferroparticles in ferrofluid has low thermal conductivity thus limiting its potential in the application of heat transfer. Increasing the volume fraction ferroparticles is one of the ways to increase the efficiency but this will cause clogging in the flow system. The present research investigated the convective boundary layer flow of a Williamson hybrid ferrofluid over a moving flat plate with viscous dissipation effects. Magnetite (Fe3O4) and copper (Cu), taken as hybrid ferroparticles, are suspended in Williamson fluid represented by human blood are believed to improve the heat transfer capabilities of the ferrofluid. The governing equations in the form of partial differential equations are reduced to ordinary differential equations by using the similarity transformation. The Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg (RKF45) method is used to numerically solve the transformed equations obtained. The effects of the magnetic parameter, the Williamson fluid parameter, the moving plate parameter, and the Eckert number on the velocity profiles, the temperature profiles as well as the reduced skin friction coefficient and the reduced Nusselt number are analyzed and discussed. It is revealed that Williamson hybrid ferrofluid has higher heat transfer capabilities and lower skin friction compared to the Williamson ferrofluid at the same volume fraction. In addition, the magnetic parameter increases the skin friction while the moving plate parameter increases the reduced Nusselt number.
Downloads