Numerical Investigation of Ferrofluid Flow at Lower Stagnation Point over a Solid Sphere using Keller-Box Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.94.2.200214Keywords:
Ferrofluid, solid sphere, magnetohydrodynamic, magnetiteAbstract
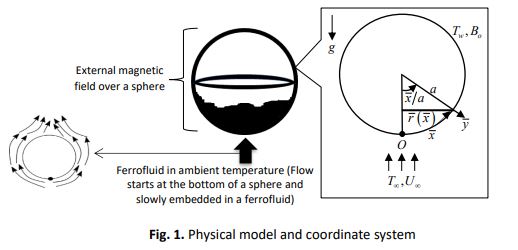
In this paper, ferrofluid flow at lower stagnation point on solid sphere is investigated theoretically by considering mixed convection boundary layer flow. The sphere surface is exposed to the magnetic field and thermal radiation by taking into account constant wall temperature boundary conditions. The discovery of the existing magnetic field near the surface while the ferrofluid flowing leads to the development of phenomenology called magnetohydrodynamic. The magnetite (Fe3O4) acts as nanoparticles dispersant and suspended in the water contained in ferrofluid are assumed as Newtonian fluid and behave as single-phase fluid flow is studied. These assumptions give physical insight into the behaviour of ferrofluid flow to be analysed and discussed. The Keller-box method is applied to solve the transformed partial differential equations numerically. The numerical results found the viscosity measured from magnetite (Fe3O4) volume fraction is the main element provided to the trend of the ferrofluid velocity flow. Besides, the ferrofluid temperature at lower stagnation point on sphere is proven influence the ferrofluid viscosity and change the velocity of ferrofluid flow.
Downloads