Impact of Magnetohydrodynamics on Hyperbolic and Walters-B Non-Newtonian Fluids
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.113.1.8294Keywords:
Hyperbolic tangent liquid, magnetic field, Walters-B liquid, spectrum relaxation methodAbstract
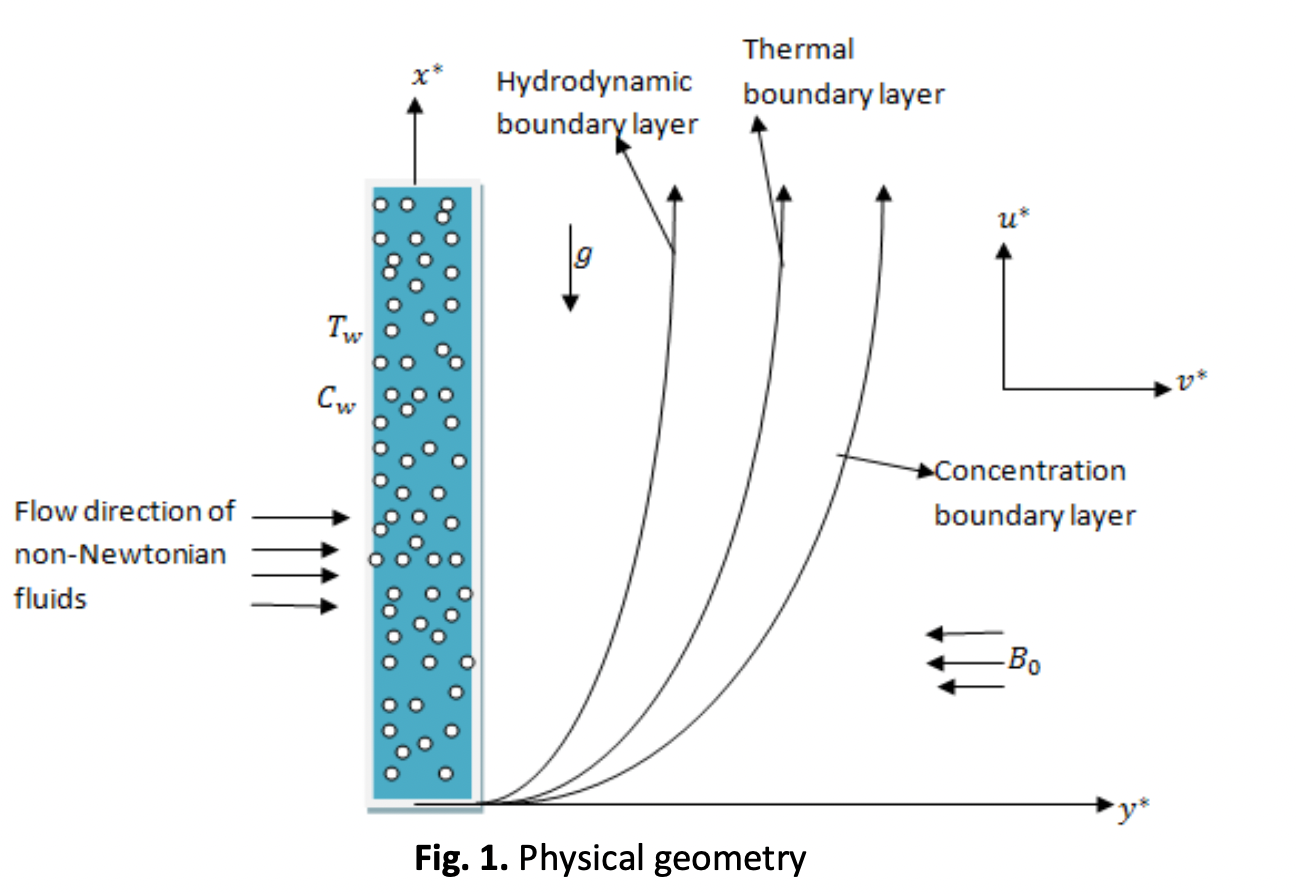
The current study examines the impact of two non-Newtonian fluids hyperbolic tangent and Walters B fluids transferring heat and mass through an upward-facing, semi-infinite porous plate into the boundary layer. PDEs are used to determine how the flow analysis works. Using the proper similarity functions, the collection of PDEs is condensed into a set of dimensionless ODEs. The spectrum relaxation method (SRM) was used to solve the simplified equations. By initially decoupling the system of coupled equations, SRM solves differential equations repeatedly. The simultaneous flow of two non-Newtonian fluids with flow characteristics including radiation, Soret, viscous dissipation, Joule heating, magnetic field, etc. is elucidated in these communications, which are regarded as being one of a kind. The electrically conductive liquids' flow direction is subjected to a uniformly strong magnetic field.
Downloads