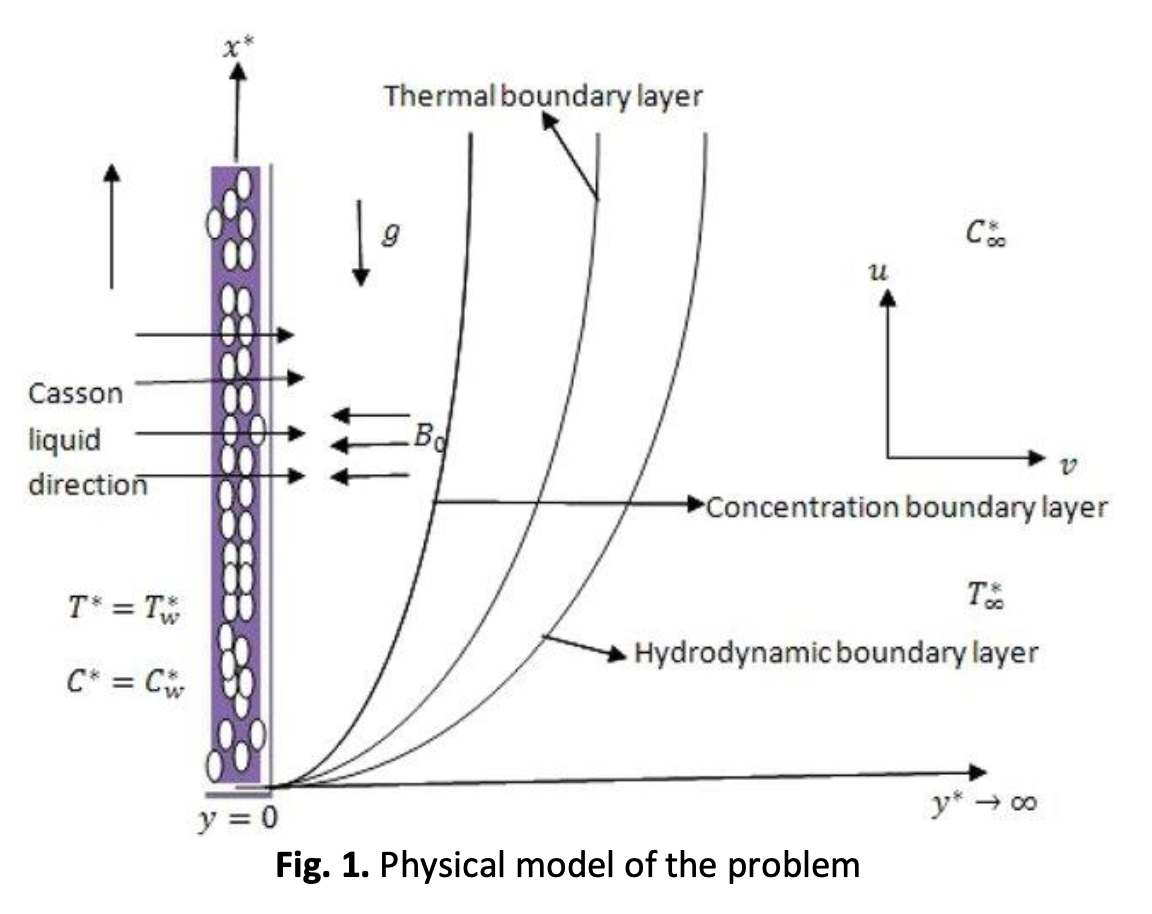
Soret-Dufour Mechanisms on Unsteady Boundary Layer Flow of Tangent Hyperbolic and Walters-B Nanoliquid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.108.1.1327Keywords:
Minimum nanoparticles, tangent hyperbolic nanoliquid, MHD, spectral relaxation techniqueAbstract
Thermal radiation, chemical reaction, and Soret-Dufour produce effects on the tangential hyperbolic and waters-B nanoliquid unsteady flow which are explored in this work due to their applications in oil and gas industry, microfluidics, aerospace and heat transfer enhancement. With the special interests in the combined Joule heating as well as viscous dissipation, the flow equations is developed to model the transport of species and thermal energy. By utilising the non-dimensional similarity variables, the equations are reduced to their dimensionless PDE form. Using the spectrum relaxation technique (SRM), the new PDES is numerically solved. The Gauss-Seidel SOR method is used to decouple and linearize equation systems. The study is carried out by investigating the graphs as flow parameters vary. It was found that the Brownian motion parameter enhances the rate of heat transfer. Furthermore, by reducing the hydrodynamic boundary layer, the introduction of magnetism was observed to decrease the speed of fluid motion.
Downloads