Characterization of a 3D Printed Self-Powered Micropump Mould for Microfluidics Application
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.97.1.127135Keywords:
Self-powered micropump, microfluidics, 3D printed mouldAbstract
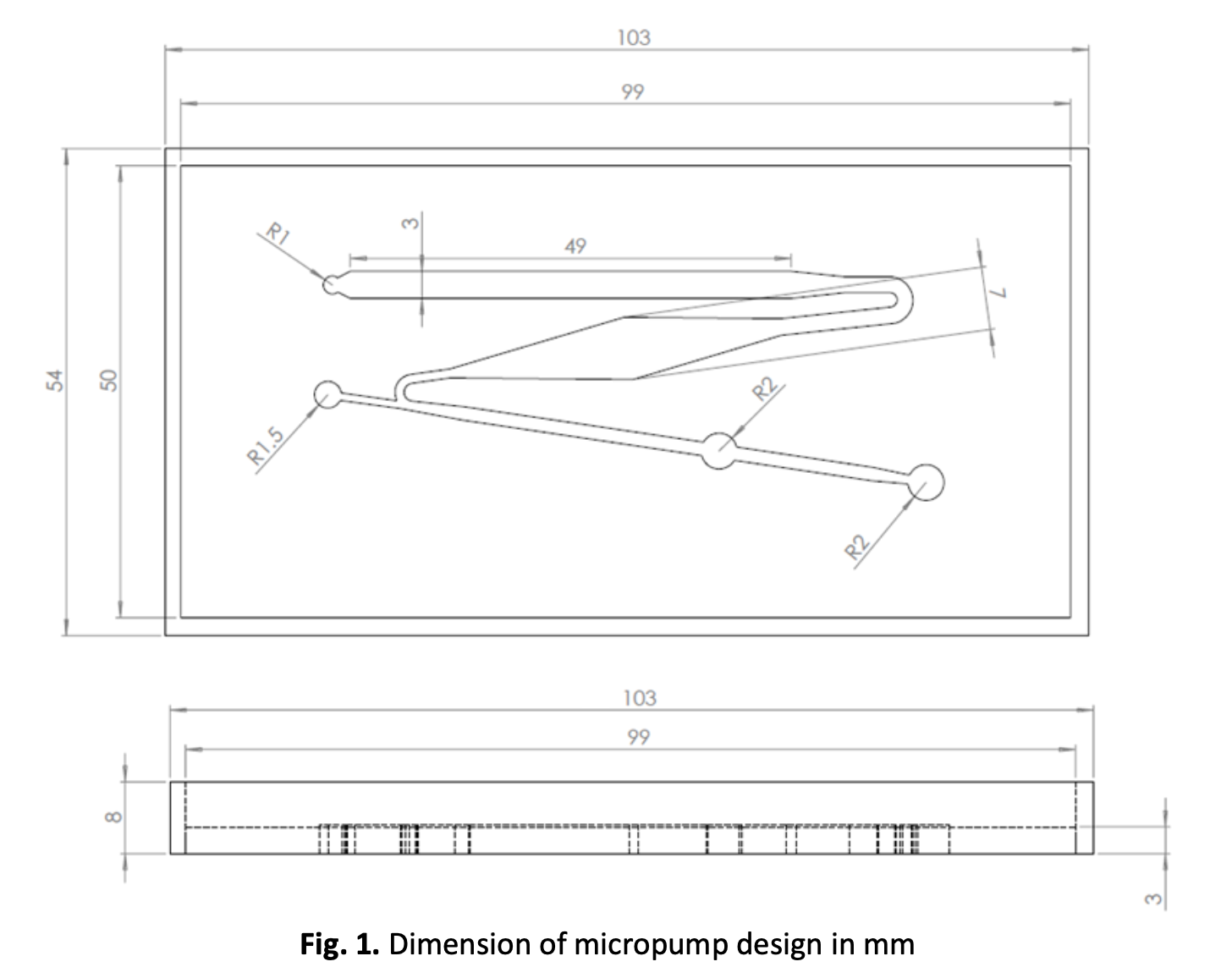
The number of words should not exceed 350 Self-powered infusion micropump is a non-mechanical micropumps for microfluidics application. A three- dimensional (3D) printing is an intelligent additive manufacturing technique that permits cheap, fast and accurate geometrically complex designs. In this study, a self-powered infusion micropump master mould was fabricated using stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing technique and was characterized accordingly. Furthermore, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) self-powered micropump from the 3D printed mould was successfully replicated using soft lithography technique. Optical microscope with i-Solution Lite imaging software was used for micropump mould dimensions characterization. It was found was that the smallest average percentage difference of 4.26 % was measured for straight inlet channel’s width between the actual mould and the computer-aided design (CAD). The average coefficient of variance (CV) for all micropump components dimensions was 3.22. It was found that the SLA 3D printing reduced manufacturing time and costs by 30.43 % and 82.84 % respectively in comparison to the standard SU-8 mould. In conclusion, SLA 3D printing technology is a viable alternative to master mould fabrication in self-infusion micropump production since it accurately reproduced the design from the CAD input.
Downloads