The Influence of Thermal Oxidation on Hardness and Microstructure of Beta-Type Titanium Alloy Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr (TNTZ)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.96.1.127136Keywords:
TNTZ, thermal oxidation, hardness, microstructure, temperature timeAbstract
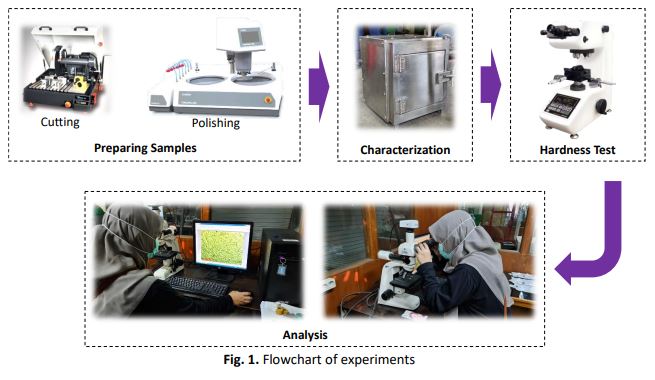
Thermal oxidation is one of the simple and low-cost methods that can improve tribological characteristics of titanium and its alloys by generating a protective layer on their surfaces. In this study, the experiment parameters were applied on thermal oxidation (TO) at 598, 673 and 723K for 40, 50 and 60s on TNTZ. The micro-Vickers hardness tests and microstructure analysis were performed for specimens before and after TO. The results exhibited that the hardness of TNTZ was increased by increasing TO temperature, but it was decreased by enlarging of TO time. Metallographic tests showed that oxidised TNTZ have equaxial β grains with a grain size approximately about 20-30μm. No significant change of microstructure (grain size) was detected after increasing TO temperature because the short time oxidation process was applied.
Downloads