Numerical Simulation of Electromechanical Impedance Based Crack Detection of Heated Metallic Structures
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.94.2.7788Keywords:
Electromechanical impedance, piezoelectric transducer, finite element, steel, aluminum, crack, temperatureAbstract
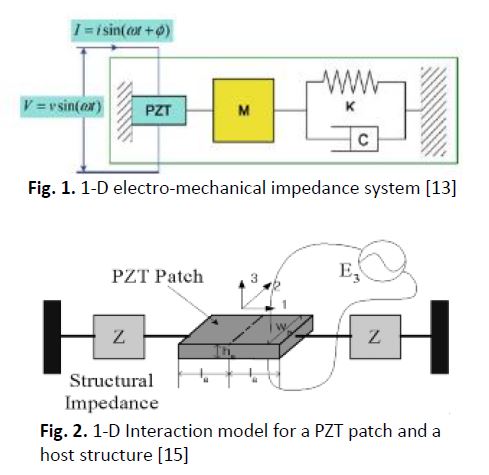
Among the many health monitoring techniques for structures, one relatively new technique is based on electromechanical impedance (EMI) measurements. The goal of this investigation was to see if the EMI approach could be used to assess the health of metallic structures. In order to achieve this objective, the feasibility of numerical simulation of piezoelectric transducer – structure interaction in the field of the EMI technique to perform structural health monitoring using commercial finite element (FE) software, ANSYS was investigated. The numerical simulations were carried out to find the effect of different types of damage such as crack and to investigate the effect of temperature on the crack detection. When compared to experimental impedance responses found in the literature, where EMI is used to monitor different undamaged and damaged structures made of steel and aluminium, the developed FE models successfully obtained similar results with good agreement. This research revealed that the FEM could be a good alternative to experimentation for studying the EMI approach.
Downloads