Experimental Study and Finite Element Analysis of Temperature Reduction and Distribution during Machining of Al-Si-Mg Composite using Deform 3D
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.97.2.825Keywords:
Finite Element Method, machining, Al-Si-Mg, nano-lubricant, temperature reduction and distributionAbstract
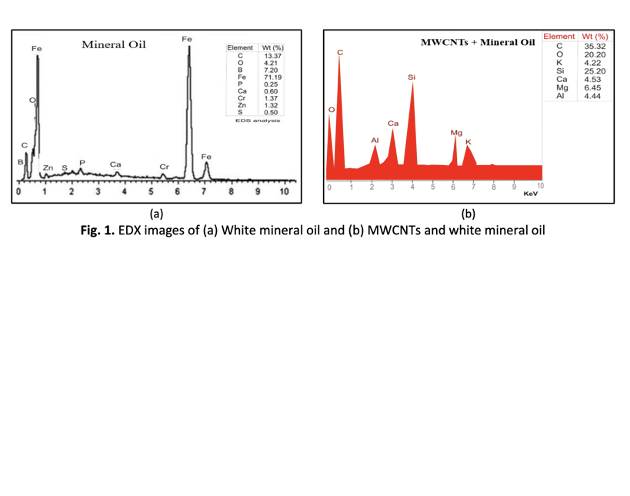
Composite materials are promising materials in the manufacturing industry due to the quality of their materials. However, in transforming these materials, the machining process experiences a high-heat generation rate, which has led to the study of temperature distribution, and reduction analysis at the cutting region. High-temperature generation during machining operation leads to thermal deformation on the developed component or parts, affecting the operation life span of the component. Thus, this study investigated the effect of mineral oil-based-Multi-walled carbon nanofluid (MWCNTs) compared to pure mineral oil in the turning of aluminum-silicon magnesium metal composite (AlSiMg) on temperature reduction and distribution. The nanofluid was prepared with 0.4g of MWCNT to 1 liter of mineral oil. The study employed the energy dispersive spectrometer to obtain the chemical composition of the developed nanofluid. Furthermore, Finite element software DEFORM 3D v11.0 uses a lagrangian incremental approach to simulate chip formation and temperature distribution on the workpiece. Also, to study the effects of the machining parameters on the temperature distribution. The experiment results showed a significant reduction of 11.9% in temperature when machining with nanofluid compared to pure mineral oil. The simulation results showed that the temperature increases as the cutting speed and feed rate increase. The minimum temperature via the DEFORM 3D Finite Element Model simulation was achieved at spindle speed 870 rpm, feed rate 2 mm/rev, and depth-of-cut 1 mm. In conclusion, the study recommends that the manufacturing industry employ the optimized machining parameters during the turning of AlSiMg metal matrix composite for a sustainable machining process.
Downloads