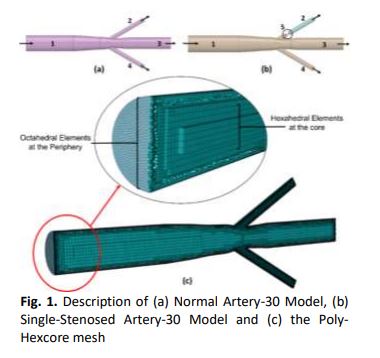
Numerical Analysis on A Non-Critical Stenosis in Renal Artery
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.88.3.3148Keywords:
CFD, Renal Artery Stenosis, Angulation, Non-critical stenosisAbstract
The increase in cardiovascular diseases worldwide has resulted in higher death rate of people globally; the primary reason being atherosclerosis. A better understanding of this condition can be achieved through the application of numerical methods to understand the haemodynamics. The present study aims to investigate the effects of renal artery angulation on the flow characteristics in a non-critically stenosed artery compared to that of a normal artery in order to understand better, the reasons for causes and progression of renal artery stenosis. Abdominal aorta-renal artery models ranging from 30° to 90° angulations were generated from computerized tomography-angiogram slices, post which they were subjected to cleanup and defeaturing. Haemodynamic parameters such as velocity, pressure and time-averaged wall shear stress were evaluated at early systole, peak systole and peak diastole for the different artery models. Extensive amounts of flow recirculation were observed in normal renal arteries with higher bifurcating angles, whereas it was not the case in stenosed arteries where flow acceleration was seen for the duration of the cardiac cycle. Evaluation of static pressure encountered a similar trend where an increase in angulation saw a decrease in pressure for normal arteries which contradicted with stenosed artery results. Analysis of shear stress saw very similar trends in normal and stenosed arteries, with lower angulation profiles experiencing higher values of shear stress at the Ostia. In the cases of arteries of higher angulation with a non-critical stenosis, the possibility of worsening of stenosis into an opprobrious stage remains a concern.
Downloads