Energy from Salinity Gradient of Wetland Saline Water Using Reverse Electrodialysis Membrane
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.101.2.4659Keywords:
Reverse electrodialysis (RED), gradient salinity, wetland saline water, power densityAbstract
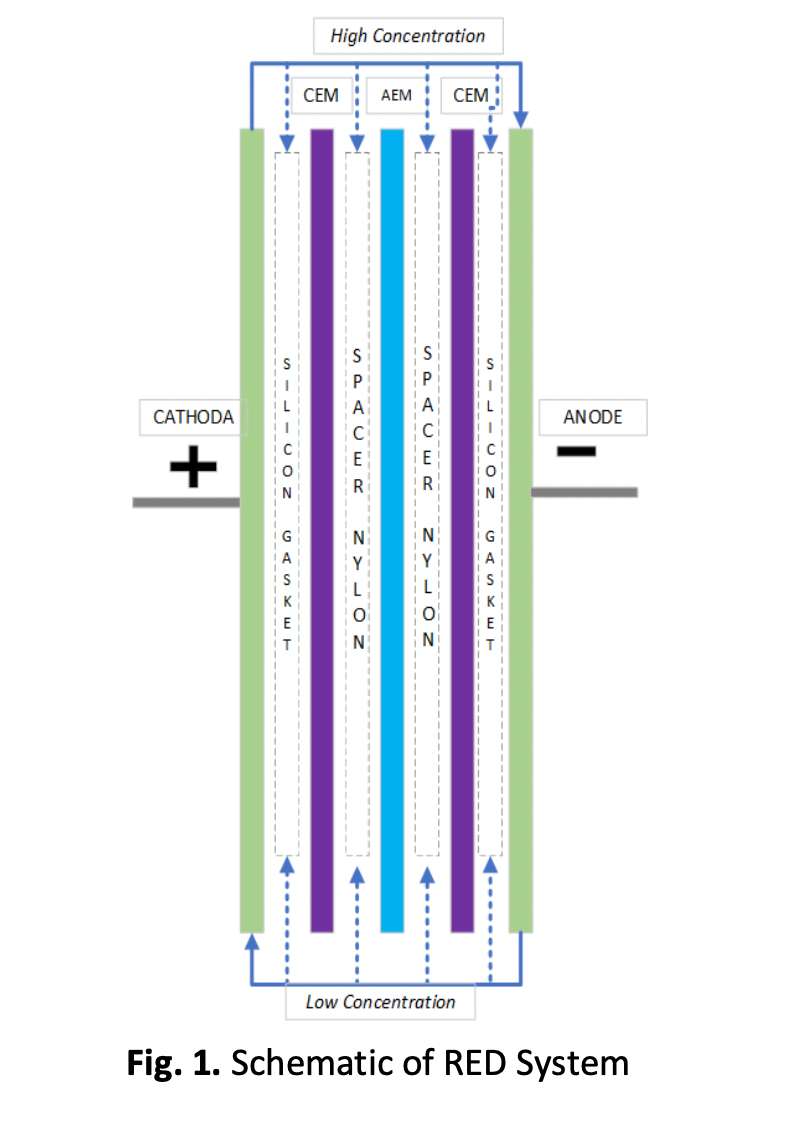
Reverse electrodialysis (RED) membrane is an emerging renewable energy which harvest electricity from mixing two streams on different salinities. In real practice is still not clearly defined for the effectiveness of salinity gradient power (SGP)-RED due to the limitation of artificial saline water. Generally, South Kalimantan Indonesia is rich by wetland and coastal area. Due to that wetland saline water is potential as saline water sources for collection the SGP. This experiment aims to investigate the impact of natural feed stream wetland saline water was collected from Muara Halayung South Kalimantan-Indonesia to demineralized (WSW),artificial brackish (ABW) (0.35 wt %NaCl), and artificial seawater (ASW) (3.5 wt % NaCl) in terms of power density measured on a lab-scale RED membrane stack prototype 12 x 12 cm. Ion exchange membrane (IEM) was used in this work consisted from cellulose modified Anion Exchange Membrane (AEM) by EDTA-quaternization (EDC) process. Whereas, Cation Exchange Membrane (CEM) was employing Nafion NR-212 with thickness 0.002 in. Lab-scale RED tests operated 3 hours into area system has 121cm2; AEM and CEM area have 100cm2; uses spacer nylon a pair between membranes; and two electrodes by stainless-steal and copper. Feed water was into RED system then measured power density as an electrical energy potential that from separate ions by AEM and CEM. The result among of this experiment, characteristic of wetland saline water naturally had electro conductivity (EC) 135.6 µS/cm; TOM 15.2 ppm; and has ionic compound higher in Na+ and Cl- which is Cl- compound as one of potentially formed salinity on that wetland water and become potential uses one of natural feed water in RED system. The highest energy power density on RED process obtained by mixed WSW:ASW was 1.43 W/m2. While ratio of the gradient salinity WSW:ABW to ABW:ASW were increasing 86% which has 1:5 to 1:30 as the effect of stream mixing by two natural feed water.
Downloads