Energy Efficiency Initiatives for A Hospital Building in Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.88.3.145155Keywords:
Hospital, energy efficiency, energy managementAbstract
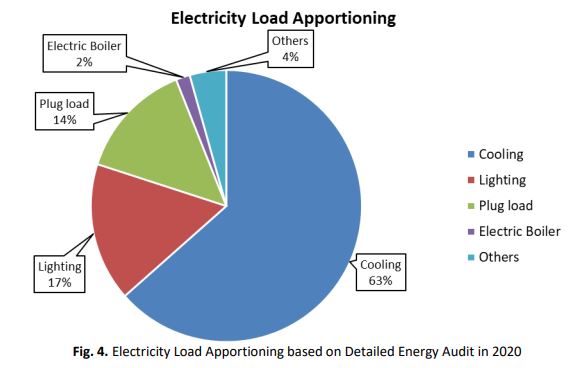
In the past decades, research about energy consumption reduction has become a trend due to concern of energy wastage that leads to the negative impact on the environment. Commercial sector produces higher energy consumption compared to other sectors in Malaysia and hospital building is one of the highest energy consumptions in the commercial sector. Continuous operation time and complexity of engineering system are some of the reasons for high energy consumptions in hospital buildings that leads to high energy costs. This study examines the electricity load apportioning for a hospital building in Selangor, Malaysia through a detailed energy audit. From the energy audit, several Energy Efficiency Initiatives (EEI) were identified in reducing the energy usage in hospital: room temperature control, efficient lighting system, efficient unit for Air-Conditioning Split Unit (ACSU) and Variable Speed Drive (VSD) installation. The EEIs is expected to produce a total electricity saving of 1,250,692 kWh/year, equivalent to a cost saving of RM 421, 706/year and total emission reduction of 869 tonnes CO2 per year.
Downloads