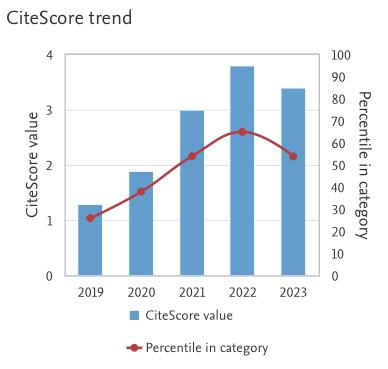
Effect of Peak Temperature on SAC Nano-Reinforced Fillet Height
Keywords:
Nano-reinforced solder, SAC fillet height, nanoparticles distribution, discrete phase model, nanocomposite solder pasteAbstract
Recently, the addition of new materials into the conventional solder pastes provides a
viable solution to optimize the material characteristics and properties of the nano
particle filled solder paste. Addition of titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles shown that
it can enable better performance of the solder. However, actual industry experiment
in terms of its optimum thermal profile for improved strength through good spread of
nano-particles in the solder is very costly and lengthy to set up. Hence, this paper
presents a preliminary study of the interaction between two models of numerical
simulation namely volume of fluid (VOF) and discrete phase model (DPM) then
compare with previous experimental data. This paper aims to analyse the effect of
peak temperature towards the fillet height of ultra-fine Sn-Ag-Cu (SAC) solder joints
doped with TiO2 nanoparticles in an electronic assembly. For the purpose of this
research, the weight percentage of the nanoparticles TiO2 with the SAC305 lead-free
reinforced solder is varied at different peak temperature and investigated in terms of
particles distribution, fillet height and thermal strain. This paper presents a 3D
numerical simulation of nano-reinforced lead (Pb)-free solder at the ultra-fine joint
component for 01005 capacitor with dimension of 0.2 x 0.2 x 0.4 mm³. The results
obtained are confirmed by conducting an experiment using a field emission scanning
electron microscope (SEM) joined with an EDS and X-ray diffraction machine. This
study concludes that the best fillet height would be obtained at 250°C. The
distributions of nanoparticles with 0.01 wt%, 0.05 wt%, and 0.15 wt% of weighted
percentage are effectively observed by using the HRTEM analysis. Based on the study,
higher temperature of the wetting region that range between 240°C and 255°C results
in better particle distributions, and fillet height of the solder by using temperature in
that range meets the requirement of IPC standards.