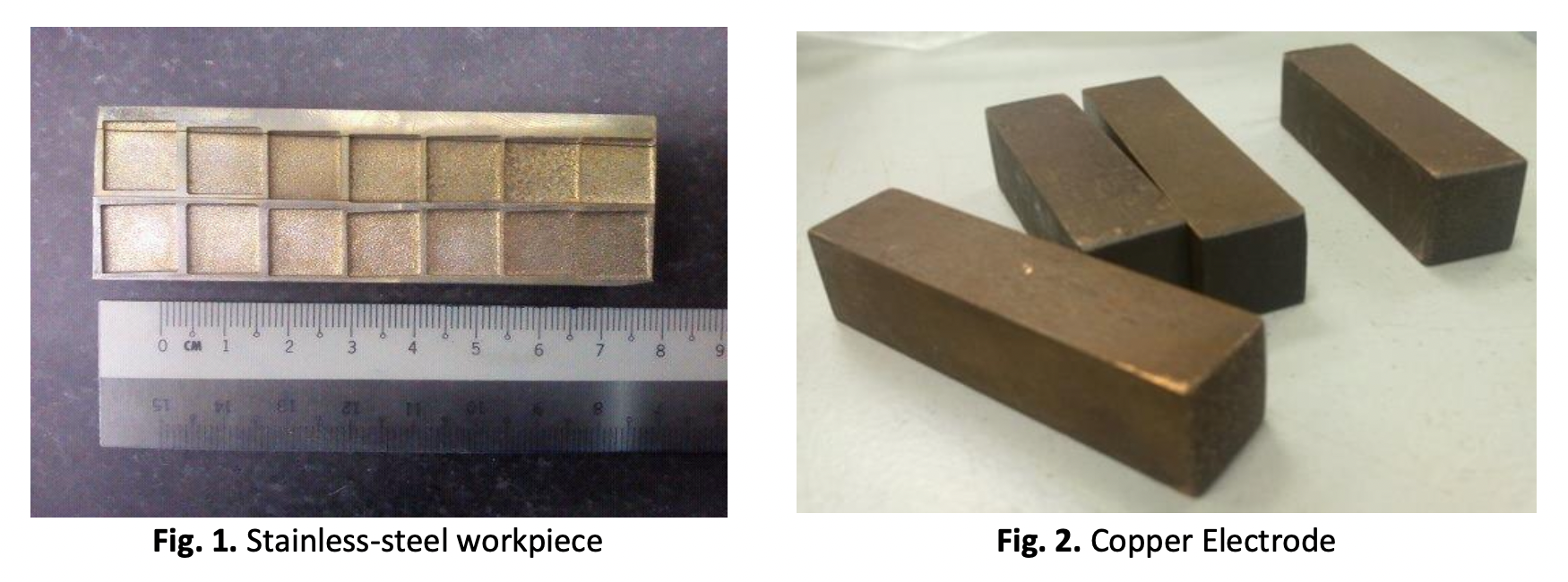
MRR and TWR Study of Powder Mix EDM and Pure EDM Based on Response Surface Methodology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.103.1.1326Keywords:
Powder-mixed electrical discharge machining, tantalum carbide powder, SUS 304 stainless steel, MRRAbstract
Powder-mixed electrical discharge machining (PMEDM) is the process of enhancing the output of the machined surface by combining dielectric fluid with various types of powders. This process is quickly gaining acceptance in the electrical discharge machining (EDM) sector. The purpose of this study is to determine whether a dielectric fluid containing tantalum carbide (TaC) powder can improve material removal rate (MRR) also lessen tool wear rate (TWR) during the subsequent EDM machining of stainless steel material. During the machining, the material removal rates, tool wear rate, and mathematical models of two different EDM mediums were examined. For the machining procedure, kerosene dielectric fluid containing TaC powder at a concentration of 25.0 g/L was used. The machining input variables were used peak current, pulse on time, and pulse off time. We determined how these variables affected the MRR and TWR of the copper-based EDMed electrode tools. During electrical discharge machining, the MRR for stainless steel (SUS 304) was increased by MRRPMEDM by 4.3 to 5.3% and TWRpEDM was reduced by 37.9% when TaC powder additive was used. Optimized results also show that TWR and maximum MRR can be achieved at 81.98% and 13.779mm3/min respectively with 83.50% desirability whenever the pulse on-time and pulse off-time are 6.20 µs and 6.50 µs respectively. The models are reliable and can be used to forecast the machining responses within the experimental region, it can be said. The MRR and TWR model for EDM with TaC powder additive (MRRPMEDM) identifies current as the most significant factor, followed by pulse on time and pulse off-time.
Downloads