Rice Husk for Adsorbing Dyes in Wastewater: Literature Review of Agricultural Waste Adsorbent, Preparation of Rice Husk Particles, Particle Size on Adsorption Characteristics with Mechanism and Adsorption Isotherm
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.106.1.113Keywords:
Adsorption, dye, isotherms, rice husk, Sustainable Development Goals, turmericAbstract
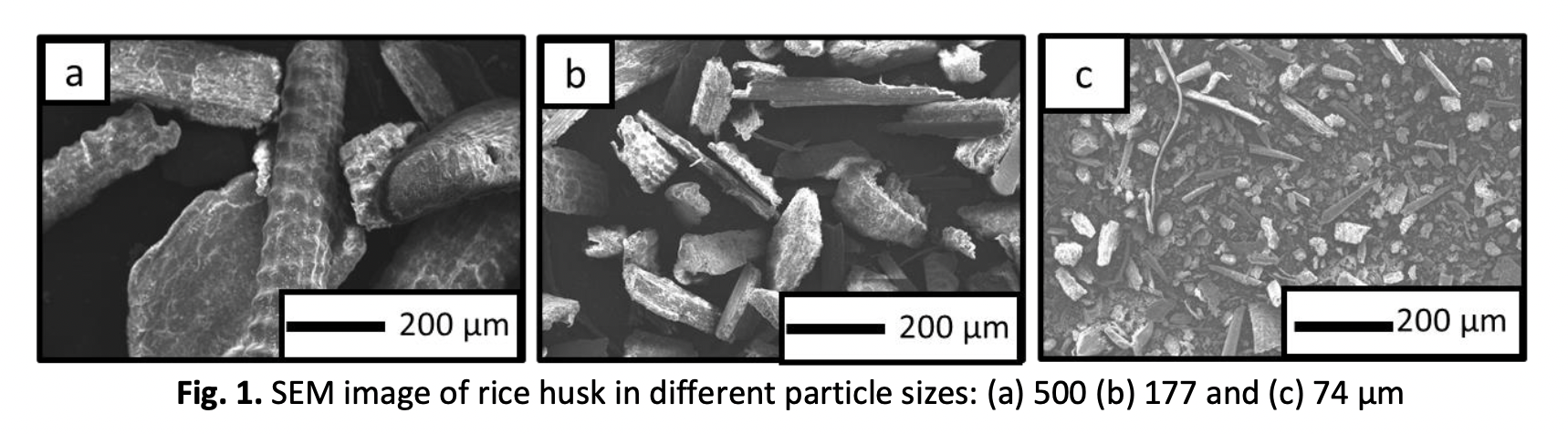
This study aims to evaluate the adsorption characteristics of unmodified natural rice husk particles (sizes of 74, 177, and 500 μm) in adsorbing dyes in wastewater. The adsorption isotherm analysis was performed in batch mode. Turmeric was selected as a model for organic dyes. Ten isotherm models were used to predict and determine the characteristic parameters: Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin, Dubinin-Radushkevich, Flory-Huggins, Fowler-Guggenheim, Hill-de-Boer, Jovanovic, Harkin Jura, and Halsey isotherm models. The adsorption isotherm analysis showed the phenomena that occur during adsorption are physical, with multilayer formation on the surface of the adsorbent and the occurrence of adsorbate-adsorbate repulsive interaction. The pore-filling molecules occur at the largest and medium particle sizes, whereas the small particle size has no pore-filling molecules. This study reveals that the natural rice husk (unmodified) could be employed as a low-cost and effective sorbent for wastewater treatment, supporting current issues in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Downloads