Crack Propagation Analysis of Fatigue Due to External Corrosion on the Construction of the Ferris Wheel in Alun-Alun Kota Batu
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.111.1.6273Keywords:
Ferris Wheel, external corrosion, stress intensity factor, crack, fatigueAbstract
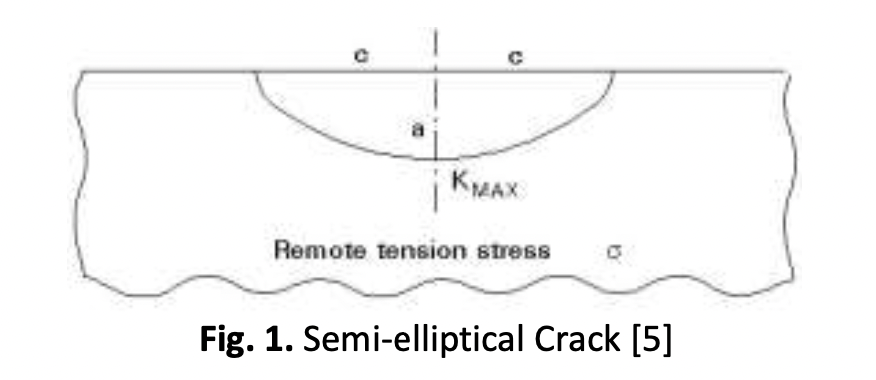
Ferris wheel is the main structure of the form from steel structure; its strength is directly related to the safety of passengers. The risk of failure due to fatigue occurs in the support pipe rods due to defects with external corrosion and cracks due to stress concentrations. Checking the crack indication at the defect point is carried out using the Liquid Penetrant Test method. Based on the inspection results, crack indications occurred at four defect location points. From the stress calculation, the value of the stress intensity factor is obtained at 4.52 Mpa√m, which still meets the fracture toughness value of 69.19 Mpa√m, from the results of the calculation of fatigue analysis, namely in the form of fatigue life at the defect location at each crack point. The structure's life span in the most resounding crack is six years, according to the minimum allowable thickness of DNV RP F01, which is 70% of its thickness. Cracks will continue to spread to structural defects with corrosion. The risk of failure will continue to increase; even total loss of the structure will undoubtedly occur if it has passed its operational design period and will be faster with dynamic loads.
Downloads