Performance Evaluation of the Developed MOF-177 for CO2 Capture
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.111.1.7481Keywords:
MOFs, CO2 capture, solvothermal method, palletization, adsorption capacityAbstract
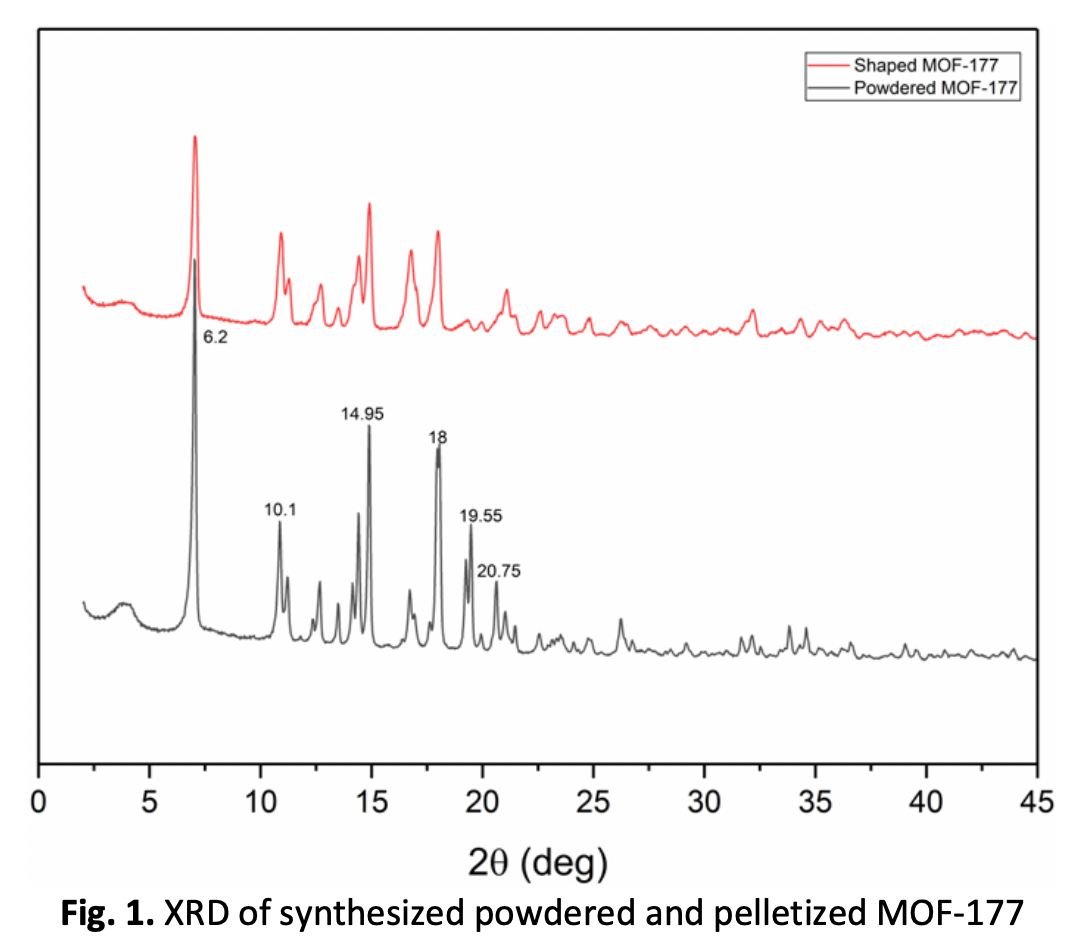
The emission of CO2 into the atmosphere has emerged as a predominant concern in recent times. Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are excellent materials that are well suited to capture CO2 due to their large surface area and pore volume. Therefore, this research involved synthesis of MOF-177 through the solvothermal method to produce both powder and pellets. The pelletizing procedure, which included the use of 5 wt % polylactic acid (PLA), was carried out using the extrusion method. To compare the performance of the synthesized MOF-177 powder and pellets, XRD, SEM, FTIR and CO2 adsorption isotherm measurements were conducted. The synthesis confirmation of powdered and pelletized MOF-177 was performed by XRD. The SEM images demonstrated that the particle size of the synthesized MOFs was between 20-25 µm, indicating that PLA was an effective binder for MOF-177. The FTIR results showed that the MOF-177 bonds and functional group present in both samples with the addition of ester groups in pellet samples due to the presence of PLA. It was also noted that by addition of PLA, the structure of MOF-177 was unaffected. Lastly, the CO2 uptake obtained from the CO2 isotherm is 0.27 mmol/g for powders and 0.47 mmol/g for the pellets. Hence, the proposed method to synthesize MOF-177 powder and pellet can be effectively used to capture CO2.
Downloads