Effects of Fly Ash Geopolymer Hot Mix Asphalt Additive on the Rheological Properties of Unaged and Short-Term Aged Asphalt Binder
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.109.1.4452Keywords:
Fly Ash Geopolymer, Hot Mix Additive, Rheological, DSRAbstract
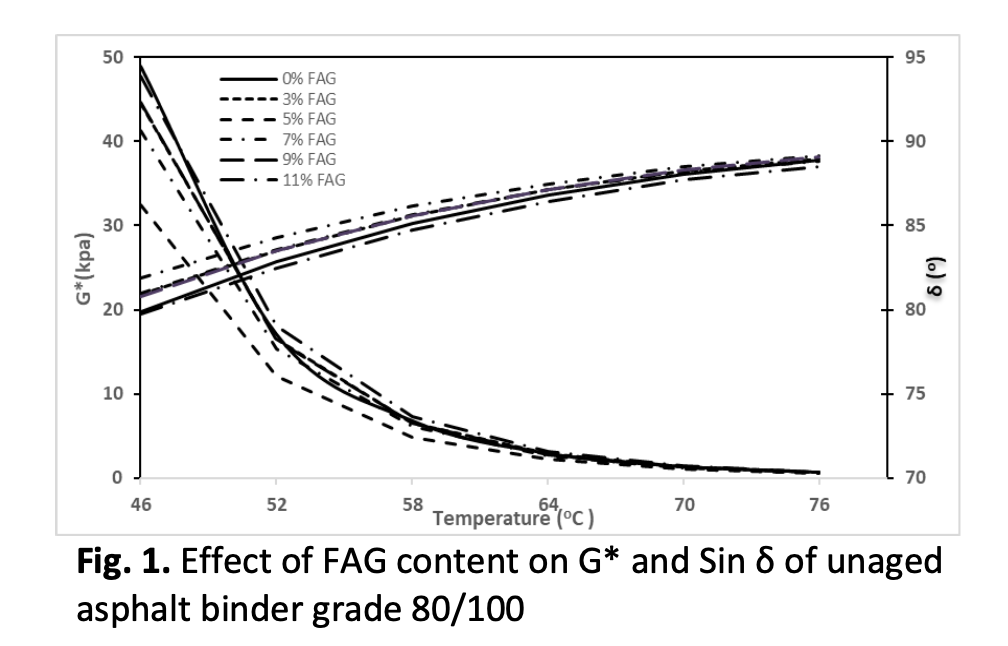
Asphalt pavement has the advantages of driving comfort and convenient maintenance, which has been widely applied to highway construction. However, due to the continuously increased traffic volume, it is recognized that asphalt binder and mixtures with enhanced characteristics are needed to guarantee the durability of the functional performance of transportation infrastructures. This study was carried to evaluate the effect of fly ash geopolymer additive on the rheological properties of unaged and short-term aged asphalt binder. In the respect, asphalt binder 80/100 and 60/70 penetration grade with 0, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11% fly ash geopolymer by weight of asphalt binder were prepared. The results indicated that the addition of FAG significantly increases the stiffness (G*) and decreases the phase angle (δ) for both unaged and short-term aged modified asphalt binder compared to the control asphalt binder. This can be proved that presence of FAG significantly improved rutting parameter i.e G*/sin δ compared to control in which capable to resist rutting at higher temperature. In terms of failure temperature, highest failure temperature of 9% FAG modified asphalt binder indicated that the binder is less susceptible to be rutting at high pavement temperature for both unaged and short-term aged, respectively. Overall research conclusions are that 9% of FAG is proposed as the minimal content to be used as an additive in asphalt binder for further mixture evaluations.
Downloads