Comparison between Lithium Substitution and Doping on the Physical and Piezoelectric Properties of Lead-Free BCZT Ceramics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.111.1.915Keywords:
Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.9Zr0.1O3 ceramics, lithium-BCZT, density, piezoelectric propertiesAbstract
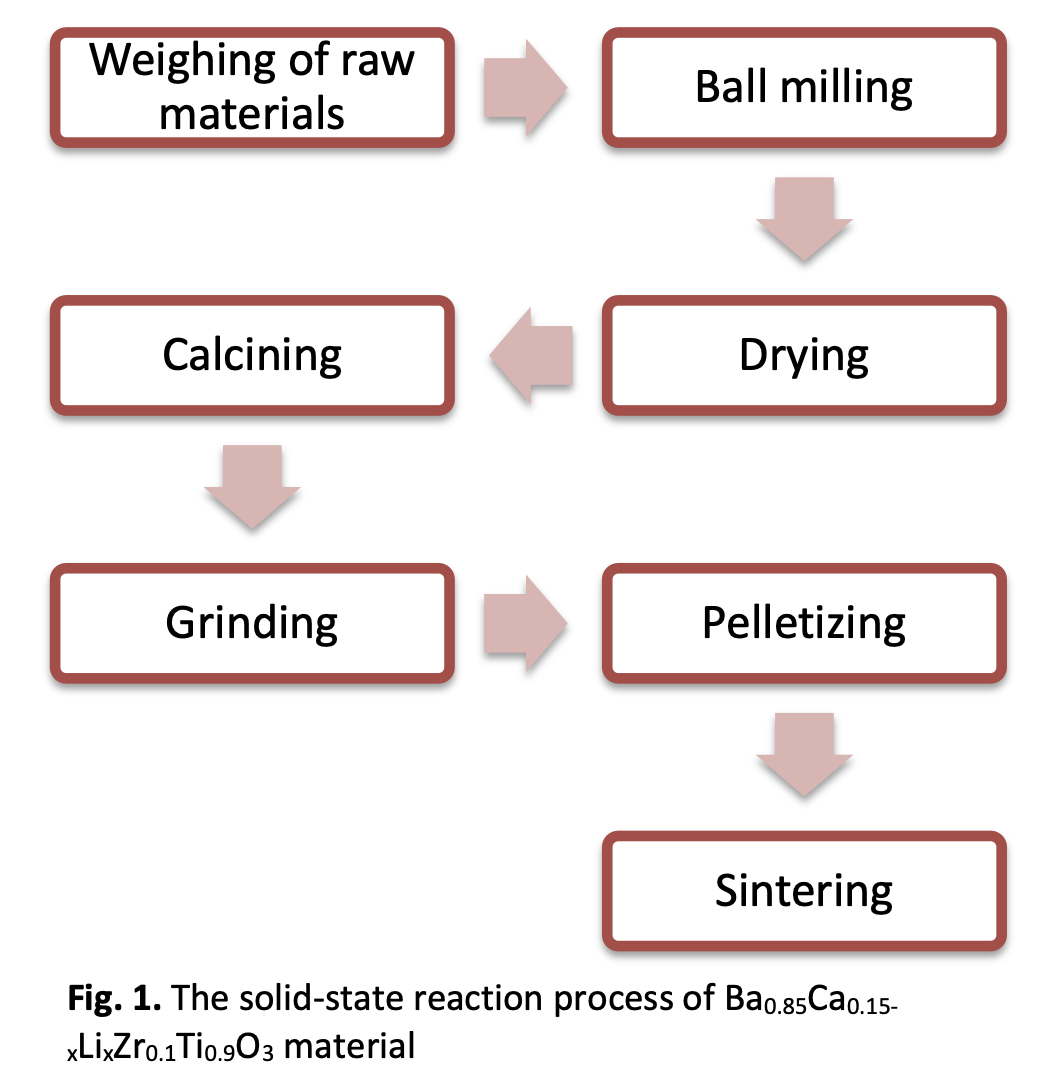
Defects generation in ceramics by element substitution or doping may improve their properties. However, different results will be obtained even though the same element is involved due to different mechanisms. Ceramics Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.9Zr0.1O3 (BCZT) is one of the potential candidates to replace lead-based material PZT. However, the conventional method requires high-temperature calcination and sintering process to synthesize this material. Thus, Lithium (Li) can act as the sintering aid to lower the temperature at the same time, the properties of piezoelectric can be enhanced. In this paper, the structural, physical, and piezoelectric performance of lead-free Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.9Zr0.1O3 (BCZT) ceramics with Lithium Li substitution and doping, synthesized by the solid-state reaction method were studied. The substitution of Li increases the density, ρ and piezoelectric coefficient, d33 of BCZT which are 4.075 g/cm3 and 304.6 pC/N, respectively. These results demonstrate that Li substitution is more beneficial to the piezoelectric properties than doping because it produces higher grain boundary resistance and activation energy and has lower conductivity than doping. This can provide a definite strategy during the chemical composition design and manufacture of BCZT ceramics.
Downloads