Analysis on the Effect of Elevated Loading of Reclaimed Spent Bleach Earth on Physico-Mechanical Properties of PLA Polymer Composite in Single Screw Extrusion Process
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.112.1.162174Keywords:
PLA composite, reclaimed spent bleach earth, extrusion process, physico-mechanical propertiesAbstract
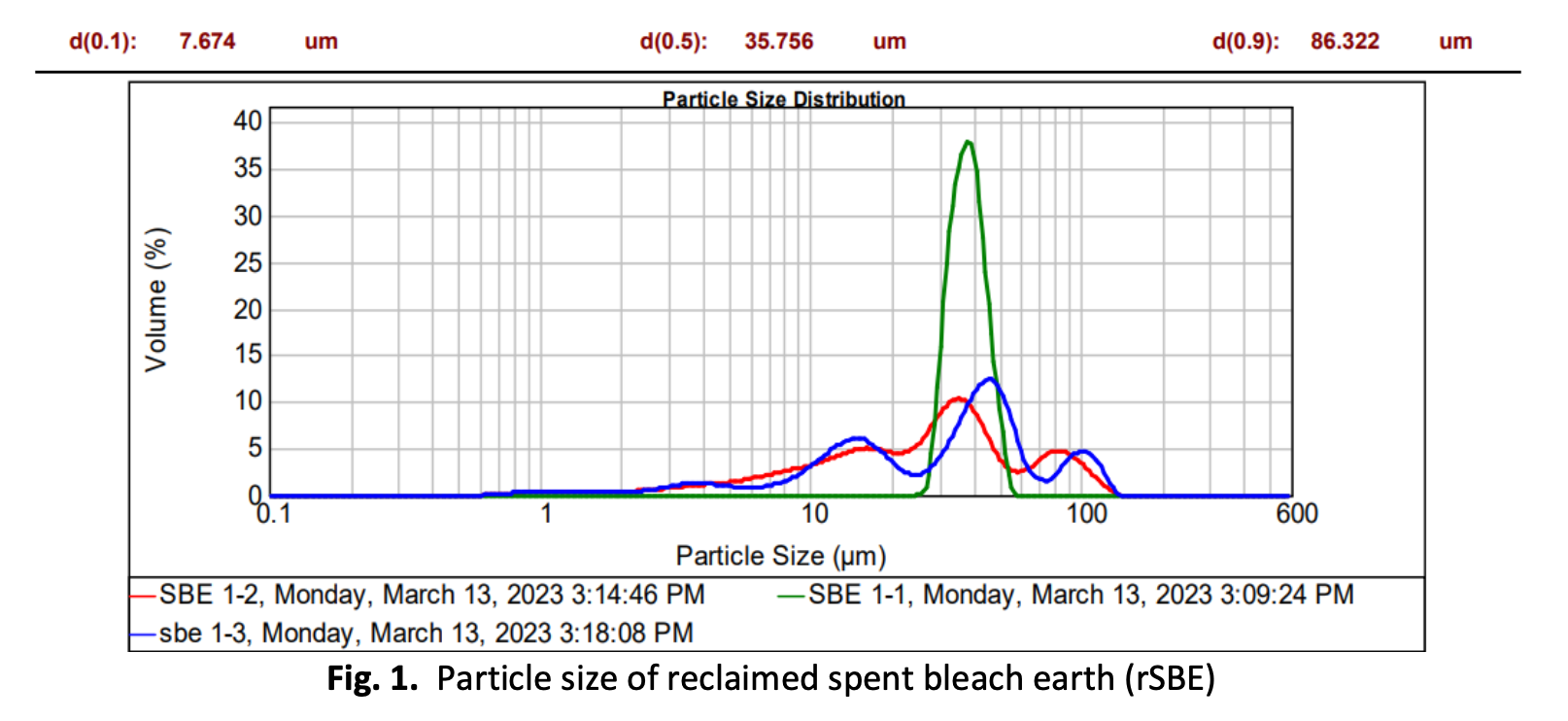
Wood has found widespread use in various applications, however, this extensive usage has resulted in adverse environmental effects, such as contributing to global warming. To mitigate these impacts, there is potential in utilizing reclaimed spent bleach earth (SBE) as an alternative source for biocomposite materials. While polylactic (PLA) polymer is biodegradable, it exhibits limited mechanical properties. This study aims to explore the feasibility of incorporating SBE into polymer matrices. Different filler loading percentages for the PLA/SBE composite (0 wt.%, 10 wt.%, 20 wt.%, 30 wt.%, and 40 wt.%) and extruder temperatures (170°C and 180°C) were considered. The SBE powder underwent characterization using techniques including Particle Size Analysis (PSA), X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), and Field Emission with Energy Dispersive X-Ray (FESEM-EDX). Characterization data revealed that SBE particles ranged in size from 40.24 μm to 51.37 μm and exhibited a crystalline structure. Density of the SBE/PLA composite directly correlated with composition, whereas tensile strength and Young's modulus displayed an inverse relationship. Moreover, varying the temperature by 10°C did not result in significant property changes. The connection between properties and SBE filler loading was evident through alterations in density and Young's modulus values. Furthermore, the composite's behavior shifted from ductile to brittle. Examination of surface fractures through fractography established a link between composite properties, filler loading, and temperature. Images of all samples displayed well-dispersed structures without significant voids. In conclusion, ANOVA analysis indicated that filler loading significantly impacted strength properties. These findings serve as a valuable addition to the existing database, which is currently limited in its coverage of SBE/PLA polymer composites, particularly in applications like packaging.
Downloads