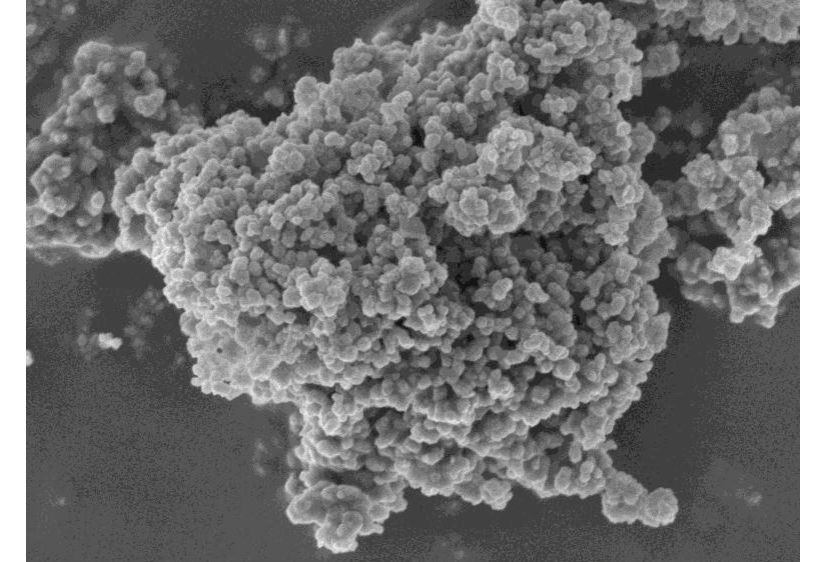
The Role of Magnesium Oxide in Enhancing Carbon Capture Ability in Cementitious Mortars
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.122.1.6270Keywords:
Carbon dioxide, concrete, magnesium oxideAbstract
Cement industries are widely used in construction and contributing around 5% to 7% of the total global carbon dioxide emission in the world. Recent research has focused on developing new types of cementitious mortars with enhanced properties. One such material that has been studied for its potential benefits is magnesium oxide (MgO). MgO can participate in the cement hydration reactions, enhance carbon capture ability, and improve the durability of cementitious mortars. This research paper discusses the impacts of integrating MgO as a cement alternative on cementitious mortars compressive strength, water absorption by capillary action, and carbonation. Two various reactive MgO samples that are readily accessible on the market were assessed as partial cement replacements (at 10%, 15%, and 20%, by weight) in the manufacture of mortars. The findings indicate that when it comes to compressive strength, it is better to have less MgO, exactly 10% or less. When water is absorbed through capillary action, it is best to use MgO values of 10% or less. In terms of carbonation protection, it is best to think about MgO concentrations of 15% or higher. In addition, the article stresses the fact that specimens with a greater content of MgO had a higher carbon dioxide absorption and a faster rate of carbonation. Overall, the use of MgO in cementitious mortars has the potential to improve their properties and reduce their environmental impact.
Downloads