Laboratory Study of Aging Characteristics of Binder Warm Mix Asphalt Chemical Additive: Rutting, Fatigue Resistance, and Chemical Composition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.121.1.146162Keywords:
Asphalt aging, chemical additives, Rheological, Aging Index, SARAAbstract
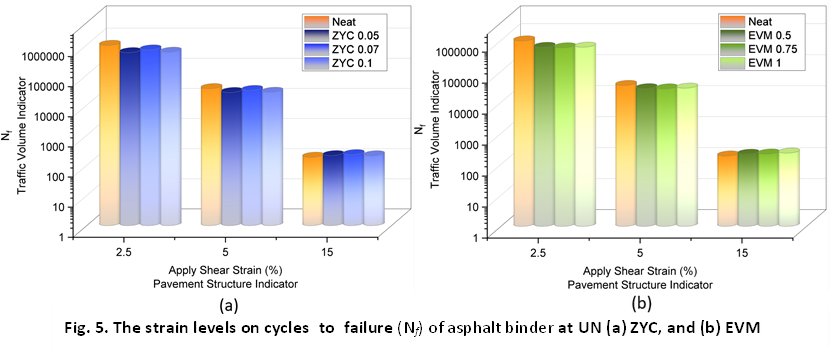
The research aims to comprehensively assess the impact of anti-stripping agents ZycoTherm (Zyc) and Evotherm M1 (EM1) on Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA). The study employs a range of laboratory tests to investigate the rheological and chemical properties of modified asphalt. Conventional tests such as penetration and softening points are employed alongside advanced techniques including Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR), and Linear Amplitude Sweep (LAS) analyses to delve into the rheological properties. Chemical properties (SARA) were analyzed using thin-layer chromatography. Both short-term aging (STA) using The Rolling Thin-Film Oven (RTFO) and long-term aging (LTA) based on the Universal Simple Aging Test are simulated under controlled laboratory conditions. It was found in conventional tests that the value changed, but not significantly. In terms of rutting and fatigue performance, Zyc 0.05% showed positive results. Fatigue behavior shows Zyc has better resistance. The asphalt fractional composition test showed changes in each age condition.
Downloads