Optimising Factors for the Production of Amorphous Rice Husk Ash via Combustion Process for Sustainable Construction: A Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.120.1.5061Keywords:
Cementitious Materials, Amorphous Silica, Acid Leaching Treatment, Rice Husk AshAbstract
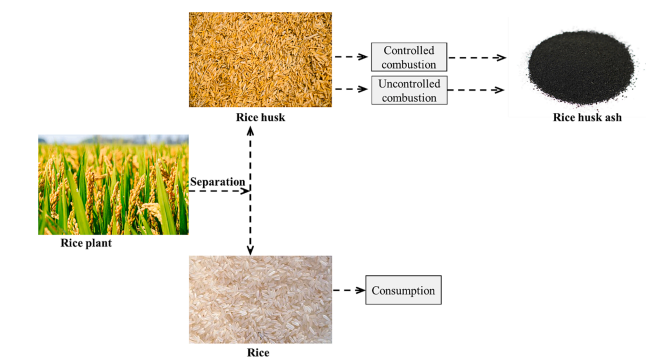
Cement is an unavoidable material in the construction industry, as it is an essential part of concrete. Moreover, its production causes serious issues related to the environment; hence, it creates a need to search for a sustainable alternative material that can be used in place of cement. On the other hand, the disposal of agricultural waste is also becoming a significant problem, and one of the materials is rice husk. Annually, about 160 million tonnes of rice husk, considered agro-waste, turn into ash due to a lack of commercial interest. Its dumping creates land pollution that poses a risk to human life. In order to tackle these problems, using agro-waste as a replacement for cement in construction can promote a green environment and make construction sustainable. Rice husk ash (RHA) is widespread owing to the large amount of silica present. However, impurities such as alkali metal oxides and uncontrolled combustion decrease the quality of silica and promote silica crystallisation because, at higher temperatures, the alkali metals, mainly potassium oxides, dissociate and act as a crystallisation catalyst. This paper briefly reviews the factors that can optimise the production of highly amorphous silica content in rice husk ash by the combustion process. It was concluded that the important parameters that can increase the pozzolanity of RHA are leaching conditions, combustion conditions, and grinding conditions. Furthermore, it has also been figured out that some areas, like understanding the reaction kinetics of RHA, an efficient leaching process, and suitable grinding conditions, need to be explored to increase the production of highly amorphous silica.
Downloads