Kinetic Hydrolysis of Cellulose Biopolymer by Carbon Nanotubes Immobilized Cellulase
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.30.3.325333Keywords:
Cellulase, Carbon-Nanotubes, Carboxymethyl-Cellulose, kinetics, viscosityAbstract
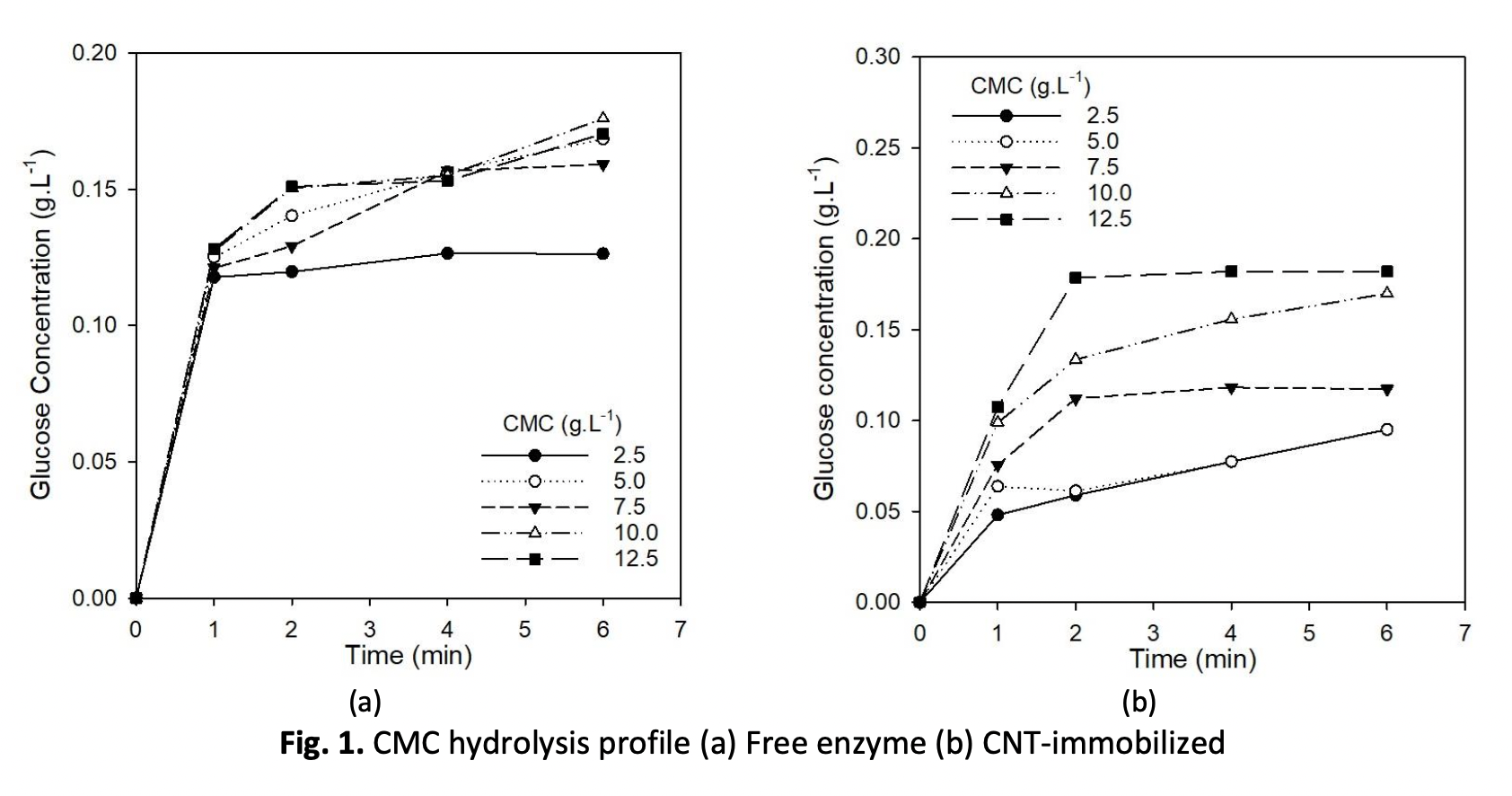
Immobilized enzymes are widely used in various biochemical reactions due to higher stability and reusability. Immobilization enzyme is a process of confinement enzyme molecules onto/within a support or matrix material via the chemical or physical process. In this study, the effect of free and CNT-Immobilized cellulase was investigated for hydrolysis of different CMC concentrations. The effect of free and CNT-Immobilized cellulase on the kinetic parameters Vmax and Km in the CMC hydrolysis was compared. The maximum reaction velocity Vmax of CNT-Immobilized cellulase is similar to free cellulase which indicates cellulase adsorption in CNT is effective in hydrolyzing CMC. However, the observed Km values for CNT-Immobilized cellulase is higher than free cellulase for different CMC concentrations. The Km value for CNT-Immobilized shows a sharp decrease in substrate affinity as compared to free cellulase due to diffusional restrictions by the CNT matrix. In addition, the initial velocity (V0) of CMC hydrolysis by CNT-Immobilized cellulase shows similar increasing pattern with the increase of reaction mixture viscosity. The current preparation of CNT-Immobilized cellulase have almost the same catalytic reaction in CMC hydrolysis as free cellulase. Thus, the current preparation of CNT-Immobilized has significant potential for green and sustainable biocatalyst in cellulose-based biopolymer hydrolysis reaction.
Downloads