Solar Irradiance and Temperature Effects on Signal Transmission Performance of LoRa Network for a Monitoring System on Island
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.37.2.2535Keywords:
LPWAN, LoRa, long range technology, environmental impact, monitoringAbstract
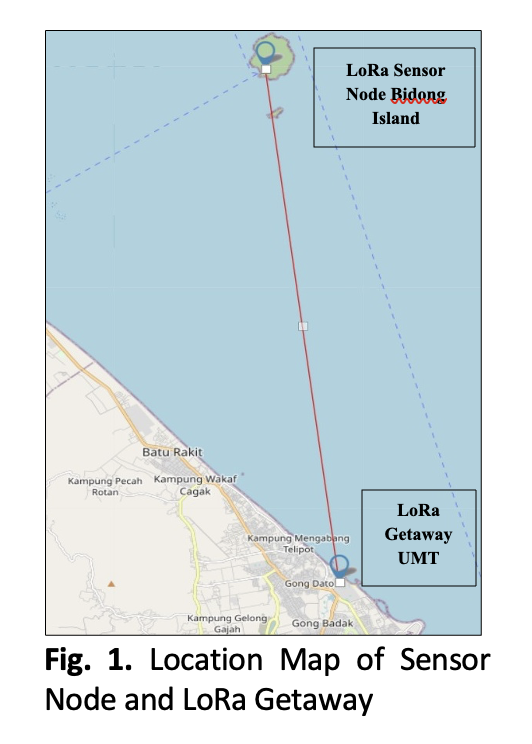
With the increasing interest in wireless technologies, Long Range (LoRa) communication is one of the most promising alternatives for providing long-range and low-power-consumption wireless networks. Low-cost, long-distance communication, and long battery life shelf, are the best description of LoRa technology which is very useful for data transmission from an island environment. This study presents the effect of solar irradiance, air temperature, and onboard temperature on the LoRa transmission signal from the sensor node (Bidong Island). Solar irradiance was obtained from online weather satellite data (Solcast) and a solar irradiance meter, while air and onboard temperature were determined using a temperature sensor and thermal imager, respectively. The findings show that higher solar irradiance significantly decreases signal transmission strength, Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). Likewise, with the decrease in onboard temperature, the RSSI signals perform better.
Downloads