A Comparative Study of Effect of Bipolar Plate Materials on Contact Resistance and Heat Transfer in a PEMFC Stack
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.1.343358Keywords:
Bipolar plate, contact resistance, gas diffusion layers, PFMFC, heat transferAbstract
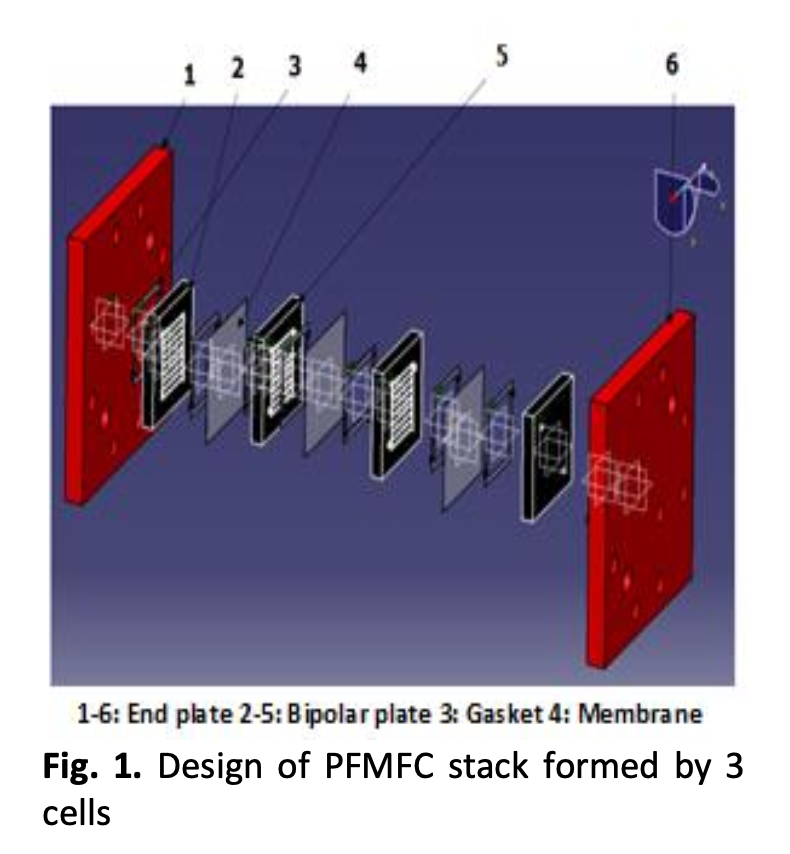
In this paper, a comparative study based on Finite Element Method has been established in order to investigate the effect of bipolar plate materials on stress and temperature distribution in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack under functioning conditions. The analysis is conducted for three bipolar plate materials: Graphite BP, stamped uncoated stainless steel SS316L, and stamped Niobium coated SS316L. ICR (Interfacial contact resistance) between GDL and BP has been measured for each BP material. The effect of current densities and clamping force on contact resistance under real operating conditions have been estimated at different cell locations in the cell stack. The results show that contact resistance GDL/BP and GDL stress depend on the location of the cell in the stack especially in case of graphite BP and corroded SS316L BP. While, the Nb coated SS316L BP allows for a neglected temperature gradient between the components of the cell stack.
Downloads