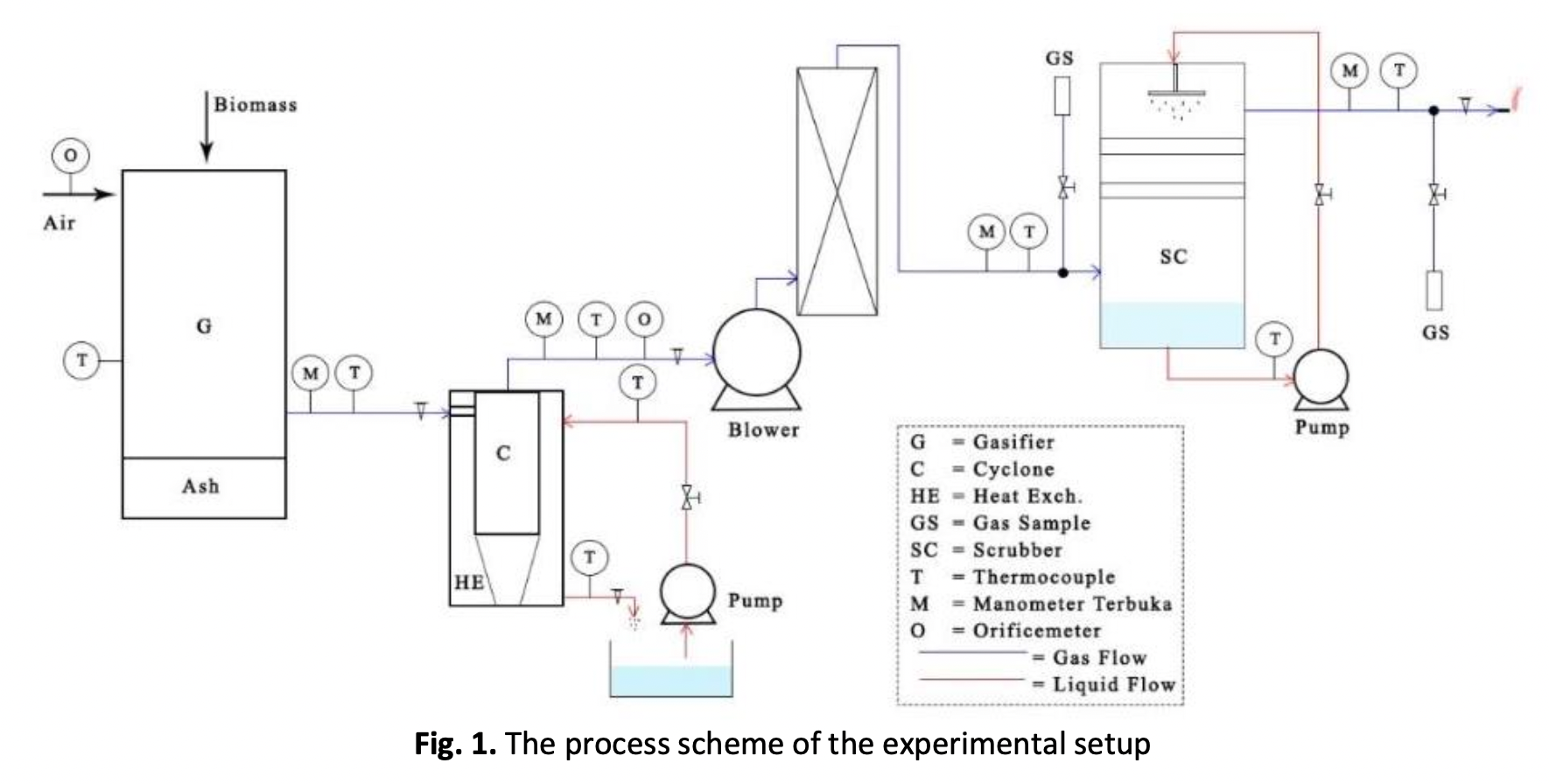
The Effect of Absorbent Type on Scrubber to Reduce Tar in Syngas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.108.1.126135Keywords:
Gasification, scrubber, absorbent, tarAbstract
Biomass Gasification is an attractive renewable energy technology. Biomass waste, as well as a renewable energy source and also, could be used as raw material to produce syngas. Nevertheless, the biomass is containing tar. The downdraft gasifier is considered to produce less tar, however, the syngas still containing tar which makes blocking and fouling of engines. Therefore, reducing tar is needed, one of them using a wet scrubber that is technically and economically viable to obtain clean syngas. Wet scrubber using absorbent to make absorption. This paper investigated the effect of variations on the type of absorbent in the scrubber to reduce tar in syngas. The absorbent used is vegetable glycerine food grade as a solvent and coconut shell charcoal with a mesh of 10-20 as a packing material. There are two variations of absorbent. Firstly, using only vegetable glycerine food grade and the second using vegetable glycerine food grade and coconut shell charcoal. Each variation was given a vegetable glycerine food-grade discharge of 31.5 ml/s. The results showed that variations in the absorbent of vegetable glycerine food grade and coconut shell charcoal resulted in higher tar removal rates is 100% in Acids, 51.88% in Furans, 65.04% in Alcohols, 35.12% in Ketones.
Downloads