Optimisation of Sapindus Mukorossi Drying Efficiency using Response Surface Methodology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.125.2.190202Keywords:
Biomass, moisture content, response surface methodology (RSM), central composite design (CCD)Abstract
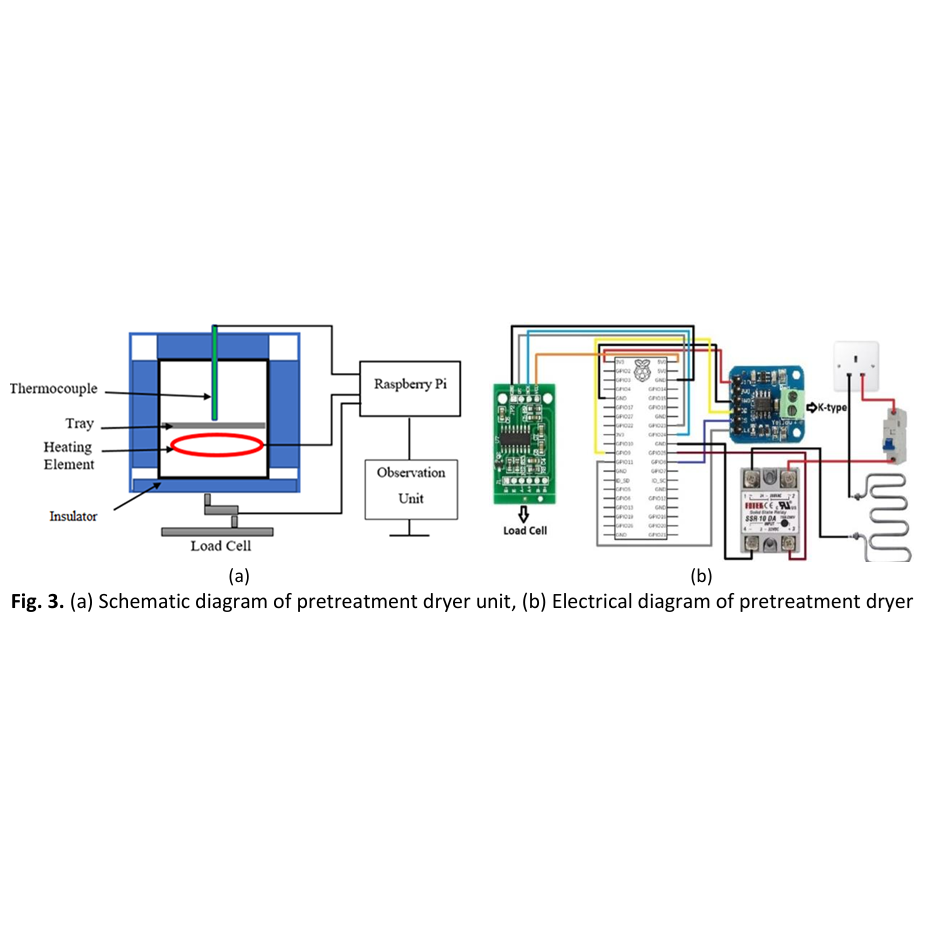
The Sapindus Mukorossi has to be pre-dried before it can be pyrolysed into bio-oil, biochar, and biogas. Traditionally, biomass is pre-dried for a full day at 105 degrees Celsius before pyrolysis. The optimum drying temperature, timing, and heating rate are essential for effective drying operation. The drying process parameters considered in the optimisation studies include temperature, duration and heating rate, and the optimisation was conducted using the response surface approach. Central Composite Design (CCD) was used to construct 20 experiment sets based on three factors (n = 3). The objective of each experiment was to observe weight reduction by applying a minimum load of 100g of Sapindus Mukorossi. The Raspberry Pi platform controlled a tailor-made 500-watt heater to adjust the temperature, rate of heating, and time. Pulse width modulation (PWM) was used to control the heating rate. The three factors and the results were generated in three-dimensional models and graphs, which finally helped to identify the best drying oven response. The optimisation method effectively resulted in a weight loss of 11.3685 g after 8 hours at a temperature of 200 °C and a heating rate of 14.15 °C/min. The CCD chooses the most efficient working parameters for the dryer to minimise operational costs. The design expert suggested a best-fitted correlation using the quadratic model with an R2 coefficient of determination of 0.9369 and a standard deviation of 0.7762.
Downloads