The Optimisation of Aerodynamic Performance Enhancement of a Flapping Wing using Response Surface Methodology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.91.1.6982Keywords:
Aerodynamics, Micro Air Vehicles, Flapping Wing, Response Surface MethodologyAbstract
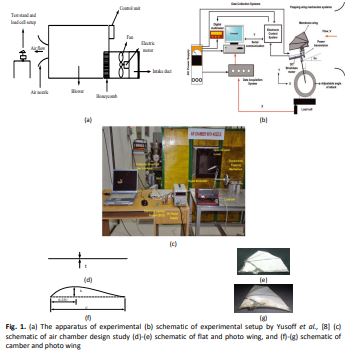
Flapping-Wing Micro Air Vehicles (FW-MAVs) are small hand-held flying vehicles that can manoeuvre in constrained space owing to their lightweight, low aspect ratio and can fly in a low Reynolds number environment. Among all wing types, flapping wings have the most potential in fulfilling this flight requirement since it offers good agility in confined spaces. However, the design problem for the flapping wings lies in lift generation and figuring out the main factors that play the biggest role in generating lift. In the present work, the effects of design parameters such as camber, velocity and frequency of the flapping wing have been investigated using the response surface methodology (RSM). The standard quadratic model of RSM called Central Composite Design (CCD) was utilized to identify and optimize the flapping wing. The experimental results were found to be in good agreement with the predicted outcomes. Out of 20 experimental trials determined by CCD, the optimum camber, velocity, and frequency were found to be 15%, 4.29 m/s and 9 Hz respectively. The experimental results in this study are reasonable and accurate and can be used for describing the aerodynamic parameters. This study also established the usefulness of RSM in optimizing the aerodynamic properties for flapping wing mechanism.
Downloads