The Evolution of Induced Drag of Multi-Winglets for Aerodynamic Performance of NACA23015
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.93.2.100110Keywords:
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Angle of Attack, Reynolds NumberAbstract
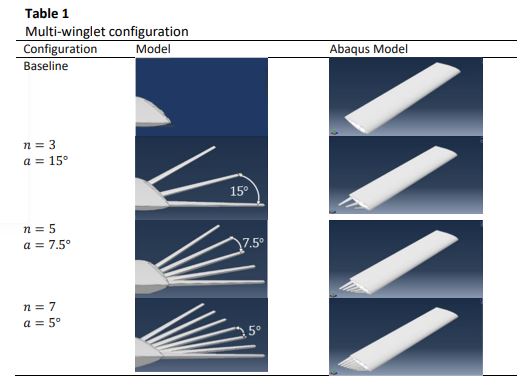
Eagle is one of the most manoeuvrable and aerodynamically efficient bird capable of soaring for a mile, and it has high gliding ratio that can reach high velocities. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles () used in military and civilian applications are required to loiter at significant altitude without being targeted by observers. However, the induced drag is usually held mainly at the wingtip, which affects the performance of the in steady state condition due to wingtip vortex. Therefore, the objectives of this paper are to study the effect of multi-winglet on different configurations in the performance of lift and drag coefficients and to analyse the flow pattern of multi-winglet with difference configurations. The wing airfoil used was with chord length of and wingspan of . The multi-winglet device was simulated using software with three, five and seven multi-winglet configurations at angles of attack between -5° to 20° (with increment of 5°) and at flying speed of . This study found that seven multi-winglets demonstrated better results in lift and drag coefficients compared to other models at low angles of attack. In conclusion, multi-winglets can improve the aerodynamic performance of airfoil in reducing the induced drag and increasing the lift coefficient, which is suitable to be implemented at low angles of attack due to the bluffing body of winglet at high angles of attack.
Downloads