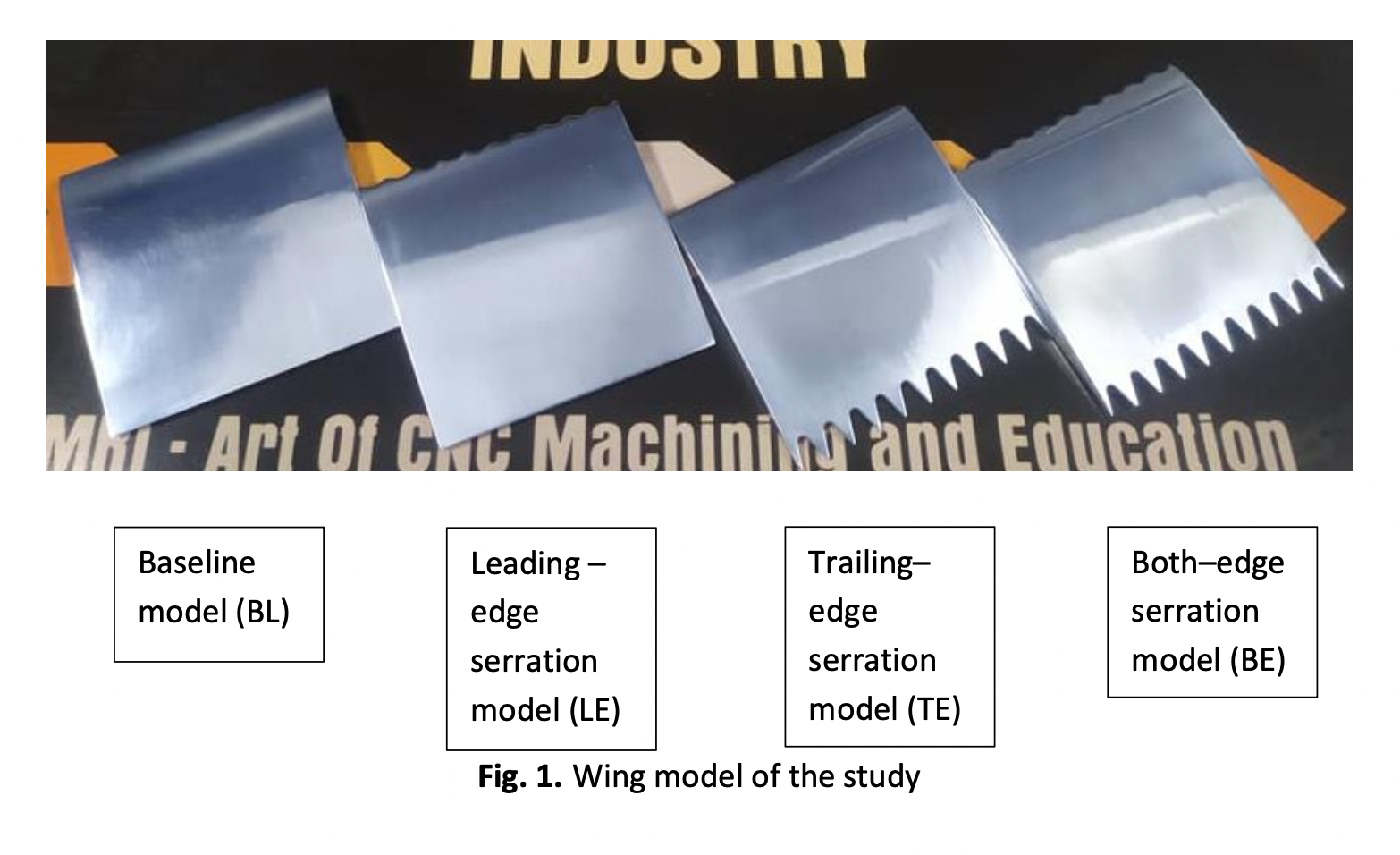
The Aerodynamic Characteristics Investigation on NACA 0012 Airfoil with Owl’s Wing Serrations for Future Air Vehicle
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.102.1.171183Keywords:
Aerodynamic performance, noise reduction, silence flight, wing serrationsAbstract
Owls have an incredibly unique ability to fly in silence, and this ability has significant potential to reduce noise pollution from aircraft engines. For decades, researchers have been studying the noise abatement system in conventional aircraft, but only a few of them had looked into the owl’s ability to reduce the aircraft noise level, especially on the serrated wing. The present study aims to investigate the lift and drag coefficient of the serrated wings including leading-edge serrations, trailing-edge serrations, both-edge serrations, and the original/baseline wing model from the NACA 0012 airfoil. The experimental testing was performed in a wind tunnel at Reynolds numbers of 20,000 and 40,000 and angle of attack from 2° to 30°, in 2° angle intervals. In general, the results showed that each wing model produced a similar lift and drag coefficient profiles, which were proportional to the angle of attack. At Reynolds number of 40,000, the lift coefficient increases from 0.45 to 1.5, as the angle of attack increases from 2° to 24°. Afterward, it decreased as the angle of attack exceeded 24°. According to the data, the trailing-edge serrations model showed the lowest drag coefficient at a Reynolds number of 40,000. Meanwhile, the highest lift coefficient at Reynolds number of 40,000 had been produced by the baseline wing model. This result is beneficial in reducing the noise generation produced by wing structure and at the same time enhancing aerodynamic efficiency.
Downloads