Statistical Analysis using Taguchi Method for Designing a Robust Wind Turbine
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.100.3.92105Keywords:
Aerofoil, design of experiment, optimization technique, Q-blade, robust design, signal to noise ratio, Taguchi method, wind turbineAbstract
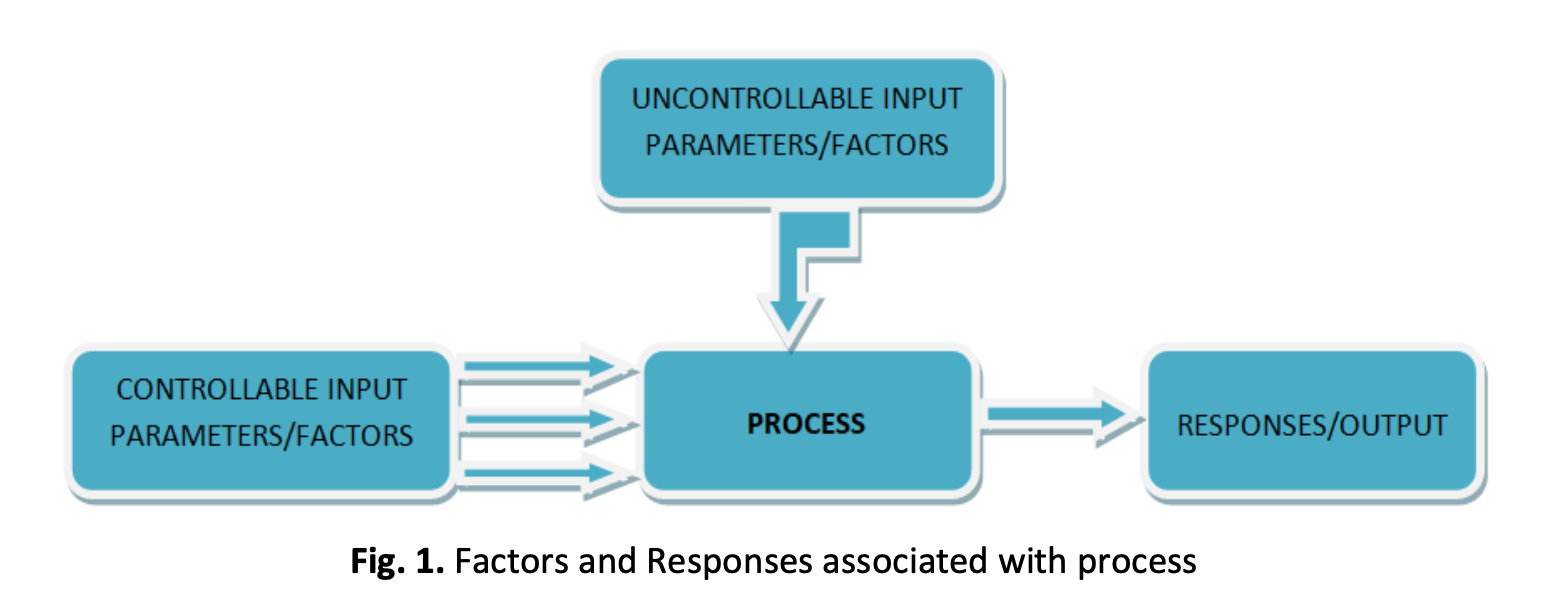
The current paper presents the tolerance and parameter design for robust wind turbine. By utilizing the traditional Taguchi method along with its extensions, there is a way of designing a robust wind turbine by considering multiple objectives, constraints and design variables. The concept of design of experiment (DOE) i.e.; Taguchi Method is used to evaluate the constrained and unconstrained problems for the optimization. The current work produces an inexpensive and simpler approach for robust vertical axis wind turbine. DOE (Taguchi Method) of L-9 Orthogonal Array having four parameters along with their three levels i.e; type of NACA aerofoil, Reynolds number, Mach number and Angle of attack are utilized for the optimization and to derive the corresponding optimal values of CL, CD and CP. The parameters like coefficient of lift, drag and power for the wind turbine was determined by Q-Blade software, which is use for designing of wind turbine blades. From the obtained results the inferences drawn were: for CL the major impact was due to Reynolds number and least was due to angle of attack, for CD the major and minor impacting factors were angle of attack and Mach number respectively and for CP the most and least influenced parameters were Reynolds number and Mach number respectively. Also, for obtaining the optimized parameters, the Grey based Taguchi method was utilized which has the combination of orthogonal arrays and grey relational analysis. The analysis showed that the NACA0021 has the maximum lift coefficient of 1.0361 and the minimum drag coefficient of 0.02190 in the case of NACA0021 aerofoil.
Downloads