A Review on Heat Transfer Enhancement of Solar Air Heater Using Various Artificial Roughed Geometries
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.89.1.92133Keywords:
Heat transfer rate, friction factor, ribs, solar air heater, artificial roughnessAbstract
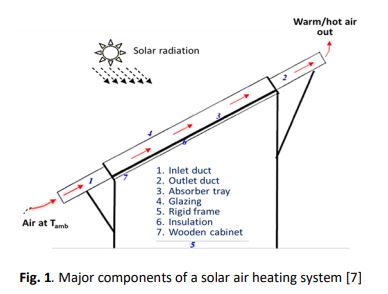
Solar air heater acts as one of the important components in utilization of solar energy. The air heater absorbs the irradiance and converts it into heat energy at the absorbing surface. The thermal energy is further use in heating flowing air through the duct. Solar air heaters are cost effective as well as simple in design. Solar air heater can be used in space heating, timber seasoning and agricultural drying. In spite of all these advantages the solar air heater has certain challenges such as the air has low heat transfer coefficient. The heat transfer rate from the heated absorber surface to the air is low. Hence in order to enhance the heat transfer coefficient the surface area either increases or the flow made to be turbulent. In order to do so the artificial roughened element must be incorporated on the heated surface. The use of artificial roughness is considered as an effective technique to enhance the heat transfer rate of fluid flowing through the duct of solar air heater. The heat transfer and friction characteristics of number of roughness geometries incorporated solar air heater have been investigated. In this paper an attempt has been made to review on element geometries used as artificial roughness in solar air heater in order to improve thermal and thermo hydraulic performance of solar air heater ducts.
Downloads