Mixed Convection Nanofluid Flow using Lie Group Scaling with the Impact of MHD, Radiation, Thermophoresis and Brownian Motion over a Vertical Wedge
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.101.2.8598Keywords:
Mixed convection, radiation parameter, Lie group scaling, vertical wedge, nanofluid, MHDAbstract
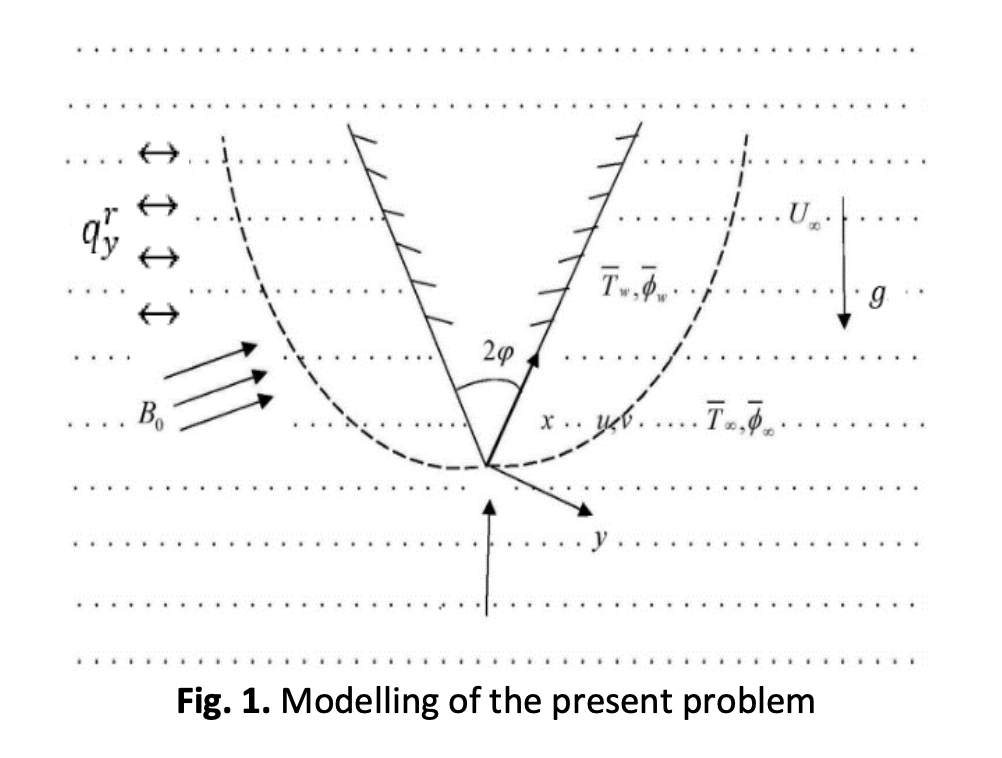
The present study concerns with the mixed convection nanofluid flow across a vertical wedge with Radiation, MHD, Brownian motion, thermophoresis effects using Lie Group scaling analysis. The governing set of highly nonlinear partial differential equations are non-dimensionalized through appropriate transformations and transformed into ordinary differential equations using Lie Group Scaling, which is solved numerically using Shooting method along with bvp4c scheme. The radiation heat flux approximated with the Rosseland approximation has been implemented in the flow equations. The influence of mixed convection, magnetic, Brownian motion, radiation, Lewis number and thermophoresis parameter on the flow profiles are examined. For establishing the efficiency of our adopted numerical technique, we made comparisons with the earlier published works and we found them to be in very good agreement.
Downloads