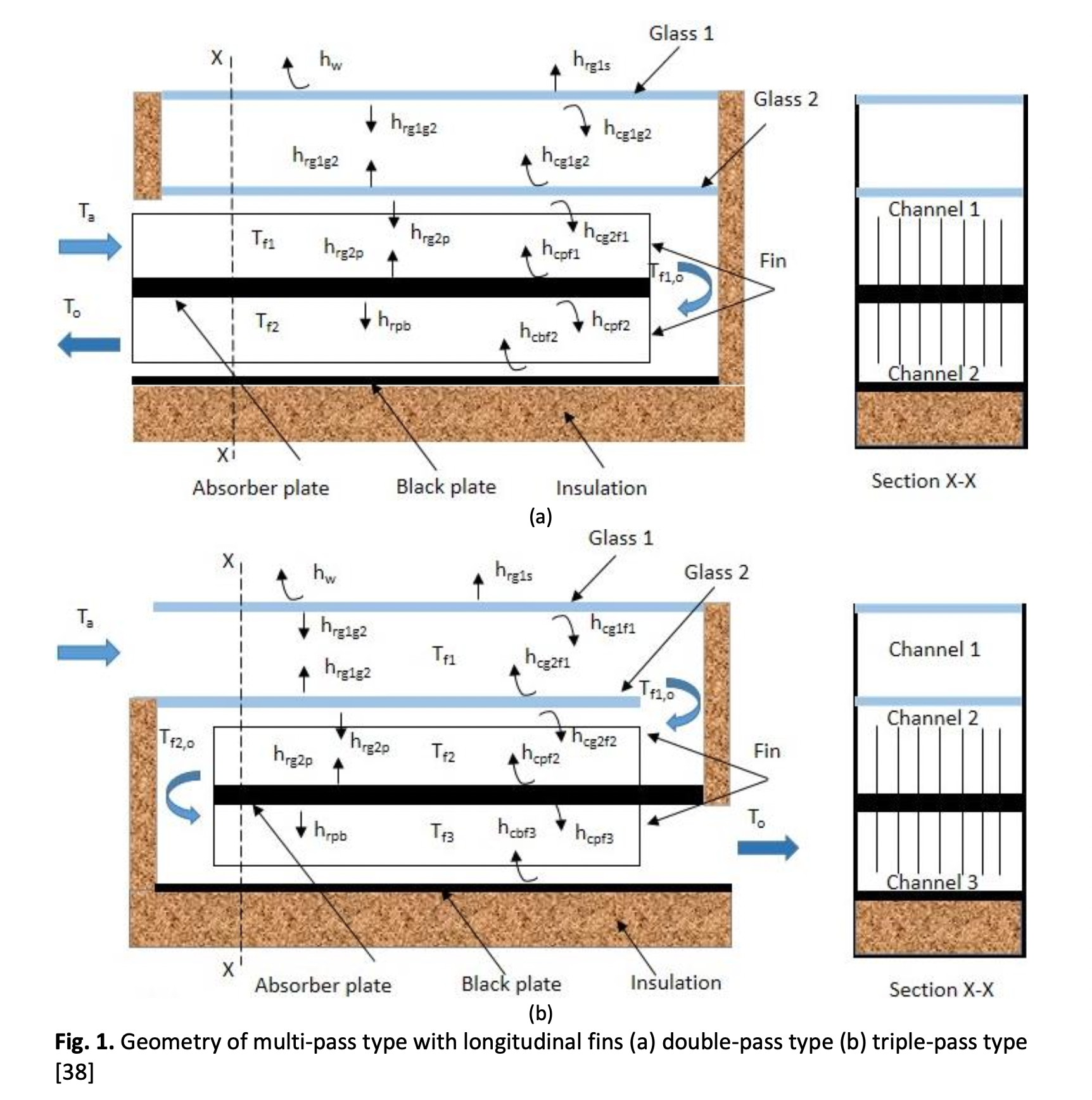
The Effective and Exergy Efficiency of Multi-Pass Solar Air Collector with Longitudinal Fins: Analysis and Optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.102.2.4265Keywords:
Effective efficiency, exergy efficiency, multi-pass solar air collector, longitudinal fins, multi-objective optimization, the PSI methodAbstract
The present work investigates the exergy and effective efficiency of the multi-pass solar air collector with longitudinal fins by analysis approach and multi-objective optimization. The effect of 0.01-0.02 kg/s air flow rate, 15-35 mm collector depth, 1-3 m collector length, and 24.21-30.67 mm fin pitch was considered. The optimization was analyzed by the Preference Selection Index (PSI) method, with three maximum criteria: thermal efficiency, effective efficiency, and exergy efficiency. Mathematical models were solved by EES software. Results indicated that the multi-pass (TPLF and DPLF) type was better than the SPWF type by three criteria. The highest exergy efficiency of the TPLF and DPLF types was 6.696% and 5.636%. The greatest effective efficiency of the TPLF and DPLF types was 69.09% and 66.17%. Furthermore, the optimization results indicated that the three efficiency criteria of the DPLF type were 58.38%, 58.22%, and 4.491% for the best case; the three efficiency criteria of the TPLF type were 60.97%, 60.85%, and 5.439% for the best case. The worst configuration was the model with a short collector length, large collector depth, and large fin pitch. The collector efficiency decreased with decreased fin pitch for the configuration with the large collector length, short collector depth, and high mass flow rate.
Downloads