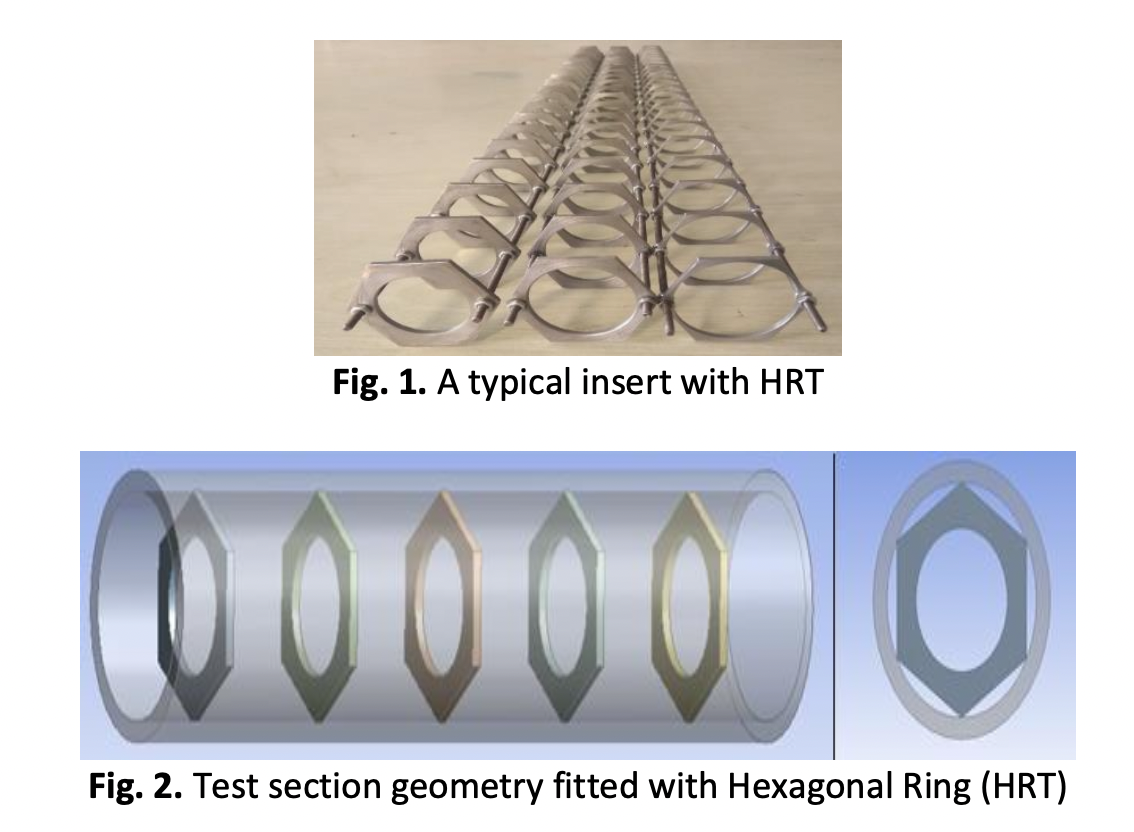
Computational Study and Enhancement of Heat Transfer Rate by Using Inserts Introduced in a Heat Exchanger
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.103.1.1629Keywords:
CFD, inserts, friction factor, heat exchangers, HRT, pressure drop, Reynolds number, Nusselt numberAbstract
The research provides a numerical and computational analysis of improving heat transfer rate in heat exchangers employing obstructing geometries such as Circular Ring, Circular Ring with` clearance, and Hexagonal ring tabulators with different pitch diameter ratios (PDR). All geometries were evaluated with flow obstruction areas of 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5. Flow obstruction area and Reynolds number were the variables that changed during the testing. The pitch diameter ratio employed in the investigation is one. The Reynolds number was changed between 6000 and 21000. For numerical examination, k--ε technique was used in this study. The use of flow obstruction geometry as a turbulator improves heat transmission derived from the hot surface of the pipe to the air throughout the test region substantially. In this research work, the tested designs, a circular ring separated from the tube wall and a hexagonal ring with the same flow blockage area improve heat transmission. Hexagonal rings incur a lower fluid friction cost than circular rings and circular rings with clearance. The maximal heat transfer enhancement (Nut/Nup) for the diameter ratio of the insert of 0.6.3 is 2.28–3.01.
Downloads