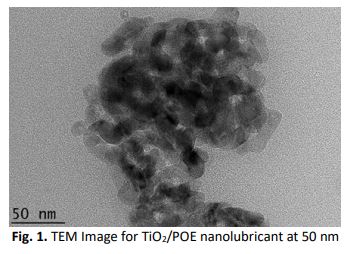
Rheological Properties of TiO2/POE Nanolubricant for Automotive Air-Conditioning System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.90.1.1022Keywords:
compressor lubricant, dynamic viscosity, nanolubricant, refrigeration, rheology propertiesAbstract
The enhancement of nanolubricant rheological properties can improve the performance of automotive air-conditioning systems. The rheological properties of the TiO2/POE nanolubricant were investigated in this study at 0.01 to 0.1% volume concentrations and temperatures ranging from 0 to 100°C. TiO2 nanoparticles were dispersed in the base lubricant of Polyol-ester (POE RL68H) lubricant in two steps. The dynamic viscosity was measured with an Anton-Paar Rotational Rheometer. According to the findings, the TiO2/POE nanolubricant behaved as Newtonian fluids at all volume concentrations and temperatures. The dynamic viscosity increment of nanolubricants up to 1.75% only occurred for 0.1% volume concentration and temperature of 90 to 100°C. Meanwhile, when compared to POE lubricant, nanolubricants with volume concentrations of 0.01 and 0.05% showed a decrement trend in dynamic viscosity of up to 1.8%. Finally, the TiO2/POE nanolubricant improved the rheological properties of the POE lubricant for use in automotive air-conditioning systems.
Downloads