CFD Analysis of Natural Convection on the Outer Surface of the Containment of APWR Model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.115.1.1929Keywords:
Computational fluid dynamic analysis, convection heat transfer coefficient, natural convection, passive containment cooling systemAbstract
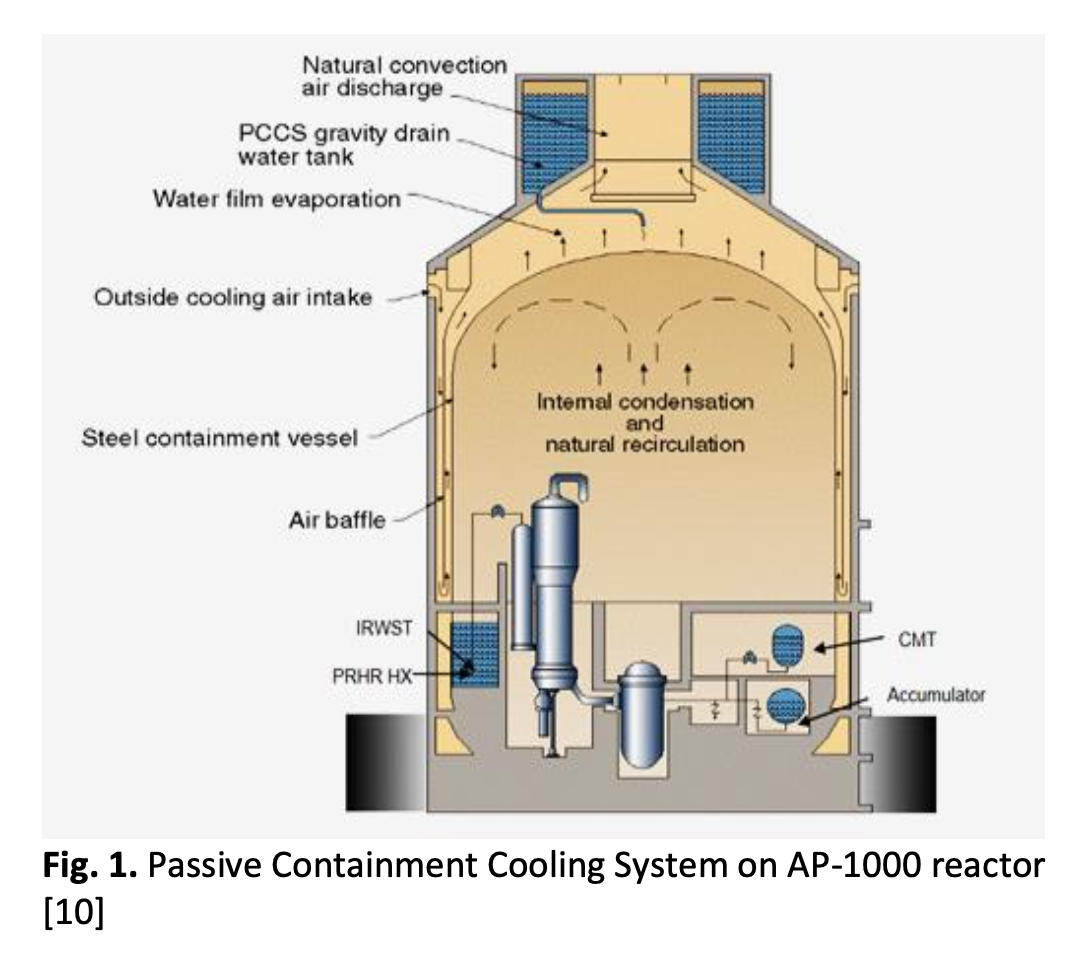
To improve the safety of nuclear power plants, a modern NPP such as Advance Pressurize Water Reactor (APWR) is equipped with a safety feature called PCCS (Passive Containment Cooling System), where naturally circulating air cools the outer surface of the containment which is used to remove decay heat released inside the containment vessel. The decay heat from the reactor core will be transferred out through the conduction mechanism and the natural convection mechanism on the outer surface of the containment vessel. Then, the hot air that forms in the gap between the containment and its baffles will rose through the chimney located at the top of the concrete building and cold air will enter through the inlet to create a natural circulation cycle. To obtain the effectiveness of the use of baffles, as a comparison, it is necessary to analyze the natural convection heat transfer on the outer surface of a containment vessel that is not equipped with a baffle. In this research, CFD analysis of natural convection on the outer surface of the containment of APWR reactor model has been done. Based on the model developed, the analysis was done to get temperature and convection heat transfer coefficient in the air flow on the containment surface. Heat flux in the containment surface varied from 500 W/m2 to 2.000 W/m2 with an increase of 500 W/m2 intervals. Based on the analysis results, the correlation equations are also proposed in this paper, namely the correlation of natural convection heat transfer for laminar regime on a vertical cylindrical with the heat flux constant in the form Nuq = a(Raq)b.
Downloads