Optimization of Reaction Typed Water Turbine in Very Low Head Water Resources for Pico Hydro
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.90.1.2339Keywords:
Low flow, low head, pico-hydro, reaction turbine, Z-bladeAbstract
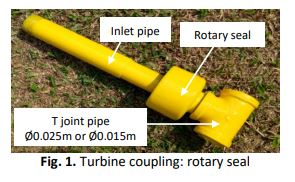
The purpose of this research is to investigate the dominant parameters that influence the optimum performance of reaction typed turbine at very low water head. The concepts of conservation of mass, momentum and energy are utilised to explore performance characteristics using a graphical technique. Parametric analysis of the governing equation and experimental results were performed to show that the turbine diameter and nozzle exit area has a dynamic response to mass flow rate, angular speed, output power and efficiency. Depending on the nozzle diameter of (0.01 m, 0.006 m, and 0.008 m) and turbine pipe size with (diameter of 0.025 m and 0.015 m), six versions of prototype turbine Z-blade turbine were produced. All the turbines have been tested at 100 kPa static water pressures and below. According to a variety of experimental data for all types of turbines, the turbine diameter and nozzle exit area have a substantial impact on turbine performance, especially at high water heads. Despite differences in turbine length and nozzle exit area, more than 90 % of the pattern curves for rotational speed, water flow rate, and mechanical power were identical. Overall, the Z-blade turbine Type B outperforms, resulting in higher turbine efficiency at low head and low flow water condition.
Downloads